C++手写AVL树全面详解
AVL树简介
AVL树的名字来源于它的发明作者G.M. Adelson-Velsky 和 E.M. Landis。AVL树是最先发明的自平衡二叉查找树(Self-Balancing Binary Search Tree,简称平衡二叉树)。
一棵AVL树有如下必要条件:
- 条件一:它必须是二叉查找树。
- 条件二:每个节点的左子树和右子树的高度差至多为1。
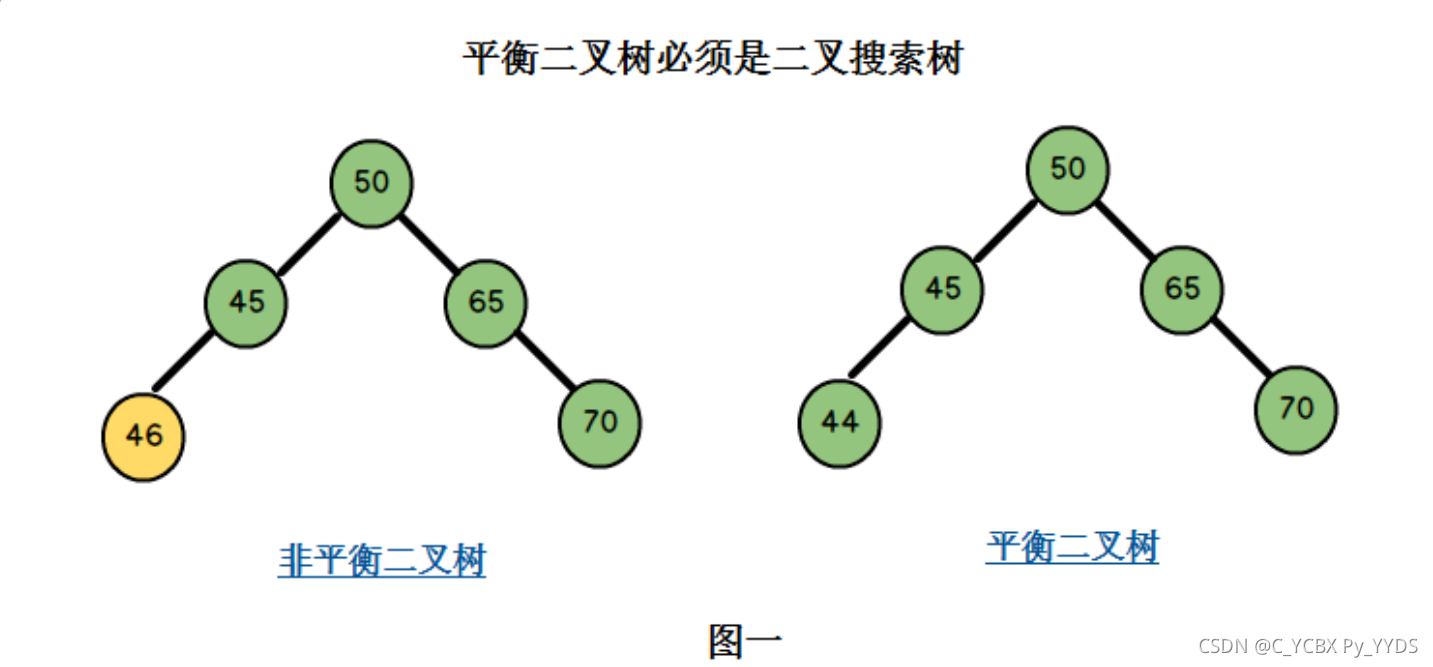
图一中左边二叉树的节点45的左孩子46比45大,不满足二叉搜索树的条件,因此它也不是一棵平衡二叉树。
右边二叉树满足二叉搜索树的条件,同时它满足条件二,因此它是一棵平衡二叉树。
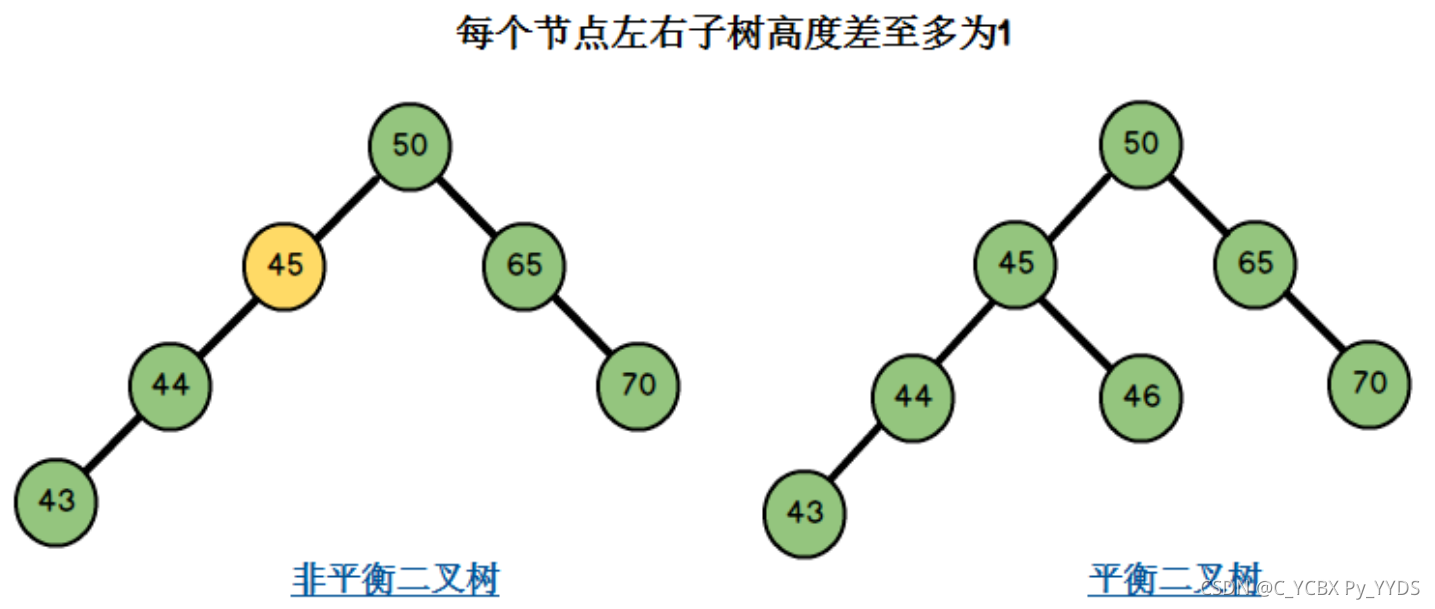 左边二叉树的节点45左子树高度2,右子树高度0,左右子树高度差为2-0=2,不满足条件二;右边二叉树的节点均满足左右子树高度差至多为1,同时它满足二叉搜索树的要求,因此它是一棵平衡二叉树。
左边二叉树的节点45左子树高度2,右子树高度0,左右子树高度差为2-0=2,不满足条件二;右边二叉树的节点均满足左右子树高度差至多为1,同时它满足二叉搜索树的要求,因此它是一棵平衡二叉树。
AVL树的查找、插入、删除操作在平均和最坏的情况下都是O(logn),这得益于它时刻维护着二叉树的平衡。但由于每次插入都需要不断的调整和维护,所以,实际上如果插入操作次数太多则同样会陷入超时的死局,最具优势的操作在于查找,因为它的底层设计使得它无论插入多少个元素,这颗二叉树总是严格平衡的,所以AVL树适用于插入操作不是很频繁,但查找操作极度频繁的情况,如果需要在插入和查找操作找一个均衡点,那么就只能选择红黑树了。
AVL树的相关概念
-
平衡因子:将二叉树上节点的左子树高度减去右子树高度的值称为该节点的平衡因子BF(Balance Factor)。 在图二右边的AVL树上: 节点50的左子树高度为3,右子树高度为2,BF= 3-2 = 1; 节点45的左子树高度为2,右子树高度为1,BF= 2-1 = 1; 节点46的左子树高度为0,右子树高度为0,BF= 0-0 = 0; 节点65的左子树高度为0,右子树高度为1,BF= 0-1 = -1; 对于平衡二叉树,BF的取值范围为[-1,1]。如果发现某个节点的BF值不在此范围,则需要对树进行调整。
-
最小不平衡树:距离插入节点最近的,且平衡因子的绝对值大于1的节点为根的子树。
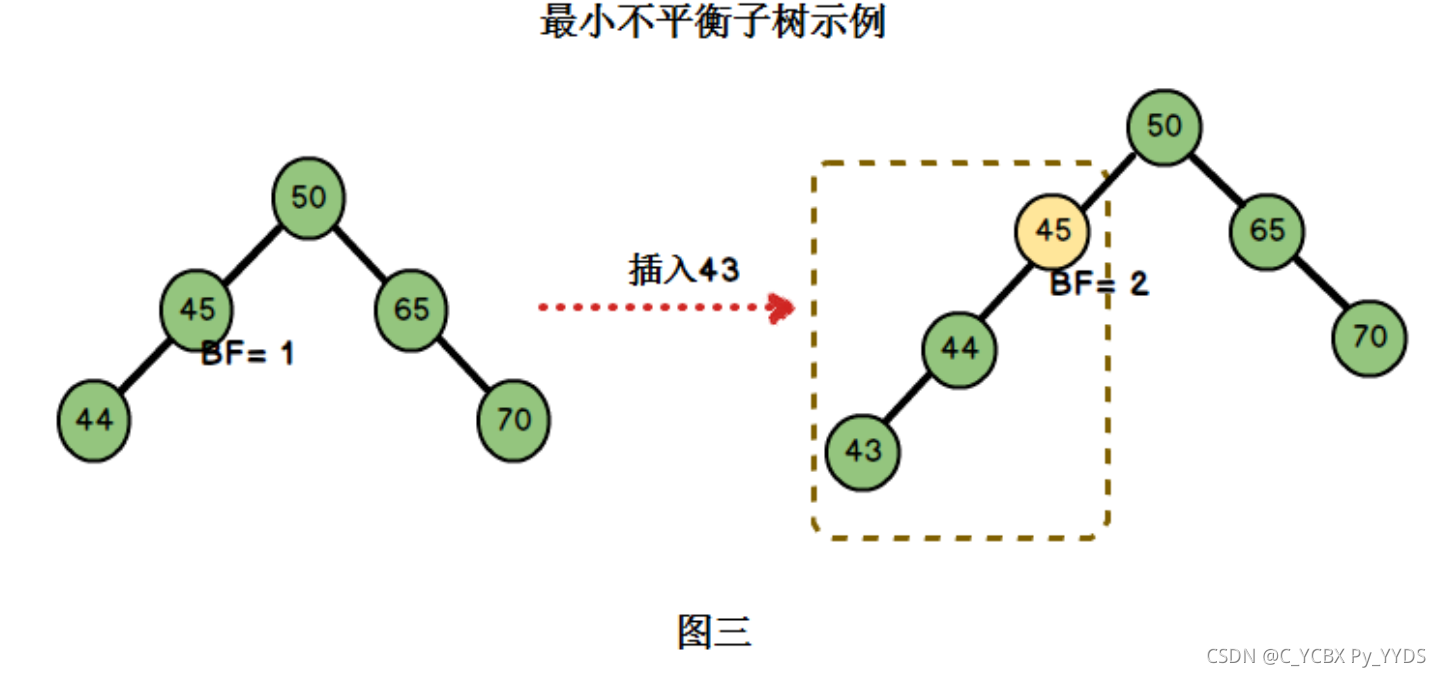 在图三中,左边二叉树的节点45的BF = 1,插入节点43后,节点45的BF = 2。节点45是距离插入点43最近的BF不在[-1,1]范围内的节点,因此以节点45为根的子树为最小不平衡子树。(这正好对应了递归的后序返回操作
在图三中,左边二叉树的节点45的BF = 1,插入节点43后,节点45的BF = 2。节点45是距离插入点43最近的BF不在[-1,1]范围内的节点,因此以节点45为根的子树为最小不平衡子树。(这正好对应了递归的后序返回操作 -
中序的前驱和后继:顾名思义,就是中序遍历下的前一个结点和后一个结点,由于时二叉搜索树,所以中序遍历的前一个结点对应比这个结点小的最大结点,而后一个结点对应比这个结点大的最小结点。(这个可以看后面代码再进行理解)这个概念在进行删除结点的操作时很有用,因为删除结点后需要同时保证仍然为二叉搜索树。 关于对前驱和后继的一些寻找方法,请看我的另一篇博客:面试题 04.06. 后继者
AVL树的实现详解
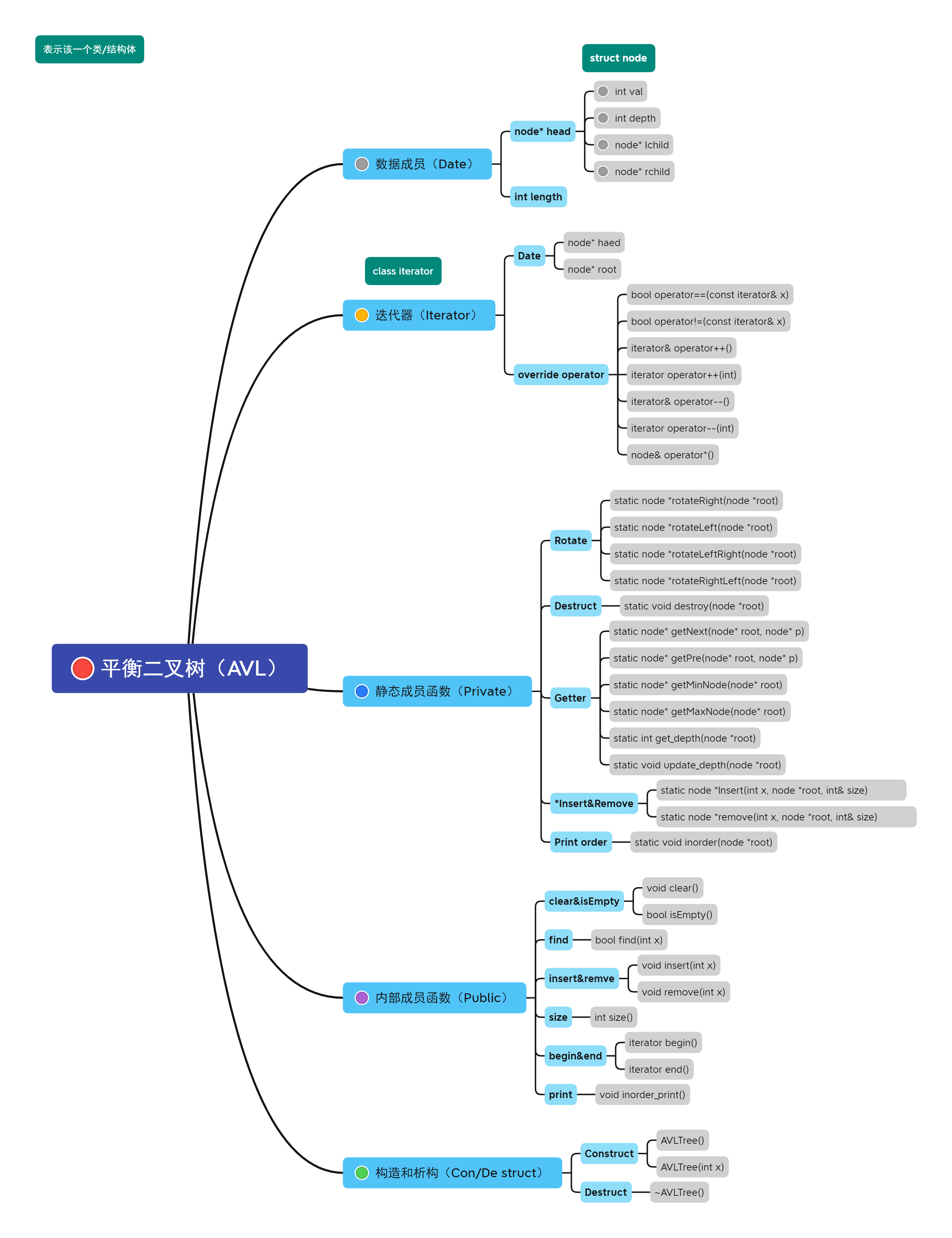
总体思维导图实现。
1. 结点结构
struct node {
int val;
int depth;
node *lchild;
node *rchild;
node() : val(0), lchild(nullptr), rchild(nullptr) {}
node(int x) : val(x), lchild(nullptr), rchild(nullptr) {}
};
- val,结点的值。
- depth,该结点的高度(它的左右子树中最高的高度+1)。
- lchild,左孩子。
- rchild,右孩子。
2. AVL树的抽象数据结构(ADT)
class AVLTree {
/*date part*/
node *head;
int length;
public:
/*construct and destruct part*/
AVLTree() : head(nullptr), length(0) {}
AVLTree(int x) : head(new node(x)), length(1) {}
~AVLTree() {
destroy(head);
}
public:
/*iterator part*/
class iterator {//封装迭代器:内部类--只能调用外部类的静态函数
node *head;
node *root;
public:
iterator(node *head, node *root) : head(head), root(root) {}
iterator &operator++();
bool operator==(const iterator &x);
bool operator!=(const iterator &x);
iterator operator++(int);
iterator &operator--();
iterator operator--(int);
int operator*();
};
private:
/*static member function*/
/*Rotate Part*/
static node *rotateRight(node *root);
static node *rotateLeft(node *root);
static node *rotateLeftRight(node *root);
static node *rotateRightLeft(node *root);
/*Destruct*/
static void destroy(node *root);
/*Getter*/
static node *getNext(node *root, node *p);
static node *getPre(node *root, node *p);
static node *getMinNode(node *root);
static node *getMaxNode(node *root);
static int get_depth(node *root);
static void update_depth(node *root);
/*Insert&Remove*/
static node *Insert(int x, node *root, int &size);
static node *remove(int x, node *root, int &size);
/*print_order*/
static void inorder(node *root);
public:
/*public interface*/
/*clear&empty*/
void clear();
bool isEmpty();
/*find*/
bool find(int x);
/*insert&remove*/
void insert(int x);
void remove(int x);
/*size*/
int size();
/*begin&end*/
iterator begin();
iterator end();
/*print*/
void inorder_print();
};
3. AVL树高度相关操作
得到高度
static int get_depth(node *root) {//得到深度
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
return root->depth;
}
更新高度
static void update_depth(node *root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return;
root->depth = std::max(get_depth(root->lchild), get_depth(root->rchild)) + 1;
}
4. 得到子树中最大/最小结点
原理:根据二叉搜索树中结点的左子树一定小于该结点,右子树一定大于该结点。
得到最大:直接遍历得出该结点的最右结点。
static node* getMaxNode(node* root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
while (root->rchild != nullptr)
root = root->rchild;
return root;
}
得到最小:直接遍历得出该结点的最左结点。
static node* getMinNode(node* root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
while (root->lchild != nullptr)
root = root->lchild;
return root;
}
5. 得到结点的前驱和后继
注意:二叉搜索树的前驱后继一般指的是它中序遍历的前一个和后一个结点,也就是从小到大排的前一个和后一个结点。
具体可以看我之前的博客--后继者
后继结点求解:如果有右子树,就是右子树的最小结点,如果没有,则是距离该节点最近的处于该节点右边的父节点。
static node* getNext(node* root, node* p) { //得到p节点的后继结点
if (root == nullptr || p == nullptr) return nullptr;
if (p->val >= root->val) {
return getNext(root->rchild, p);
} else {
node* left = getNext(root->lchild, p);
return left ? left : root;
}
}
前驱结点求解:如果有左子树,就是左子树的最大结点,如果没有,则是距离该节点最近的处于该节点左边的父节点。
static node* getPre(node* root, node* p) { //得到p节点的前驱结点
if (root == nullptr || p == nullptr)return nullptr;
if (p->val <= root->val) {
return getPre(root->lchild, p);
} else {
node* right = getPre(root->rchild, p);
return right ? right : root;
}
}
6. AVL树失衡的调整
节点的插入或删除都有可能导致AVL树失去平衡,因此,失衡调整是插入与删除操作的基础。
AVL树的失衡调整可以分为四种情况,我们逐一分析。
假设我们要为数组a[]={4,5,6,3,2,8,7,0,1}构建一棵AVL树。
情况一:左旋
首先插入{4,5,6},在插入元素6后出现不平衡的情况:
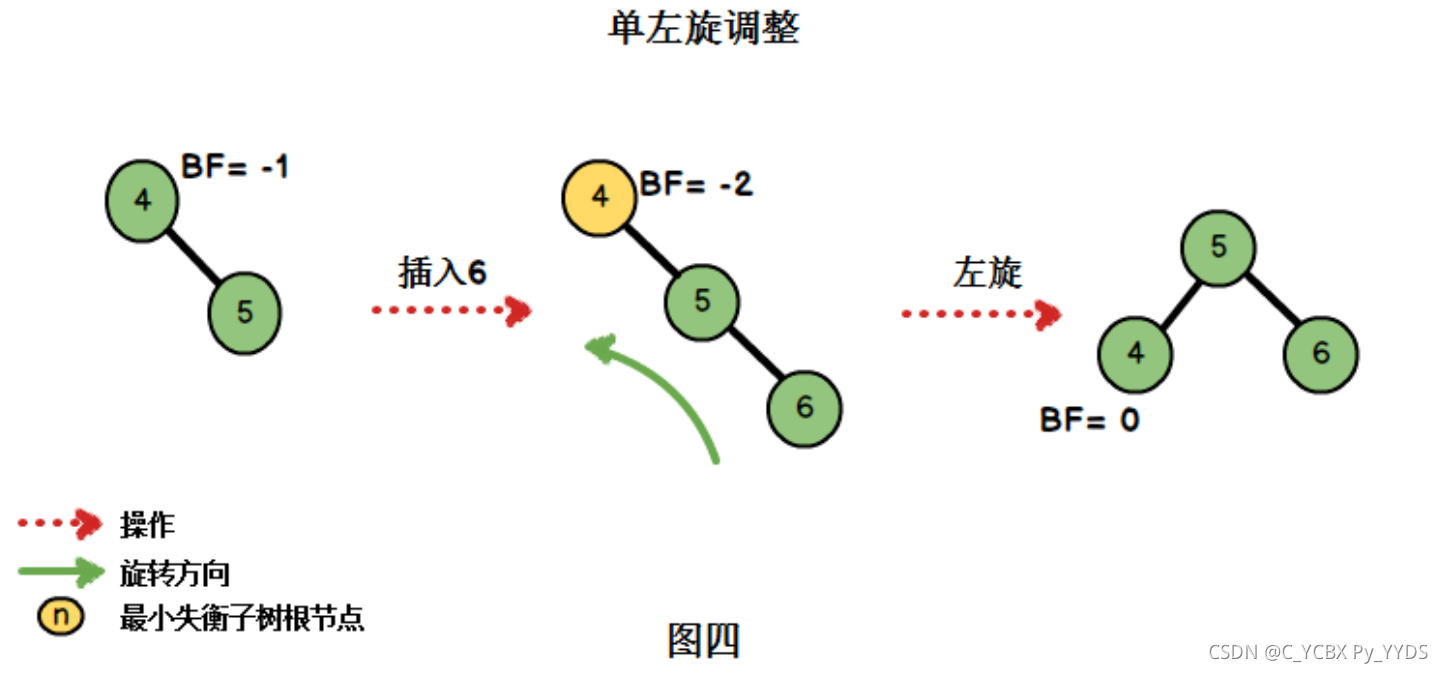
当我们在右子树插入右孩子导致AVL失衡时,我们需要进行单左旋调整。旋转围绕最小失衡子树的根节点进行。 在删除新节点时也有可能会出现需要单左旋的情况。 左旋代码如下:
static node *rotateLeft(node *root) {
node *son = root->rchild;
root->rchild = son->lchild;
son->lchild = root;
update_depth(root);
update_depth(son);
return son;
}
情况二:右旋
我们继续插入元素{3,2},此时二叉树为:
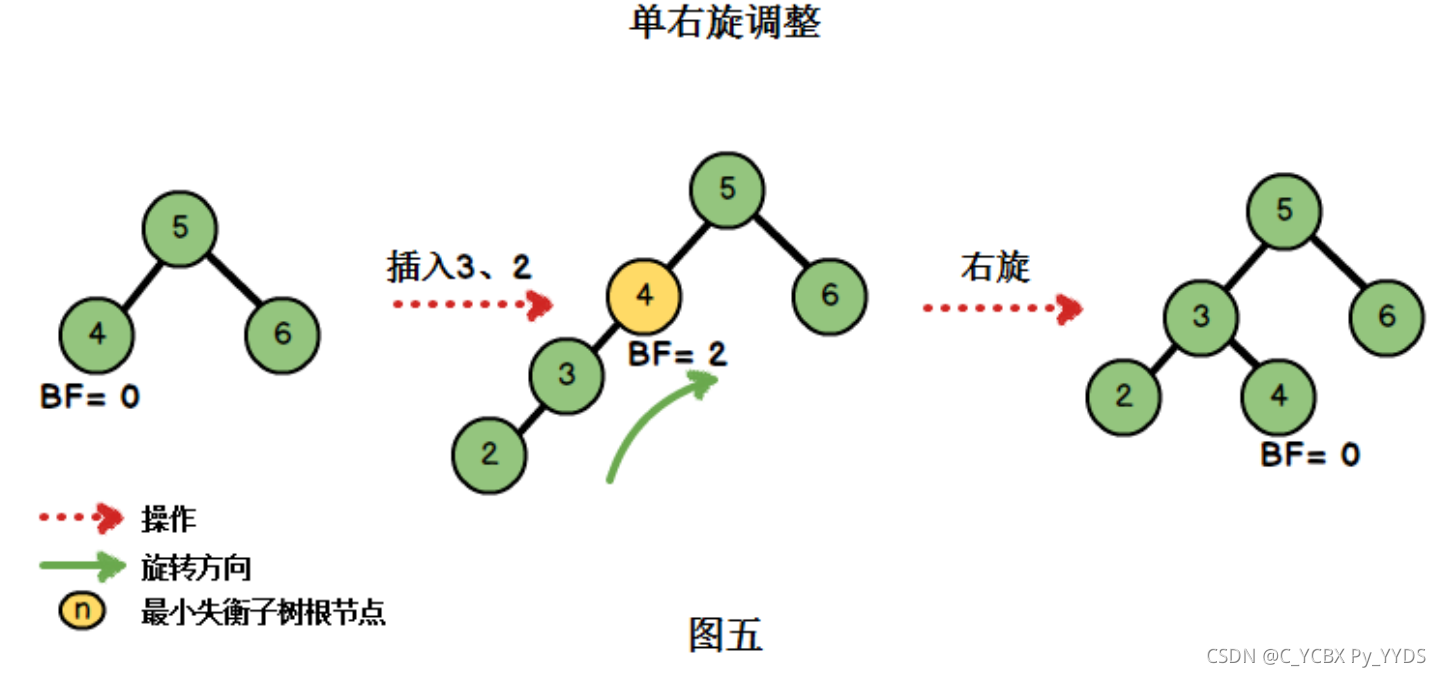 插入3、2后出现了不平衡的情况。此时的插入情况是“在左子树上插入左孩子导致AVL树失衡”,我们需要进行单右旋调整。
右旋代码:
插入3、2后出现了不平衡的情况。此时的插入情况是“在左子树上插入左孩子导致AVL树失衡”,我们需要进行单右旋调整。
右旋代码:
static node *rotateRight(node *root) {//右旋
node *son = root->lchild;
root->lchild = son->rchild;
son->rchild = root;
update_depth(root);//更新深度(右旋只会对这两结点产生影响
update_depth(son);
return son;
}
情况三:先左旋后右旋
需要进行两次旋转的原因是第一次旋转后,AVL树仍旧处于不平衡的状态,第二次旋转再次进行调整。
我们继续插入元素{8,7}
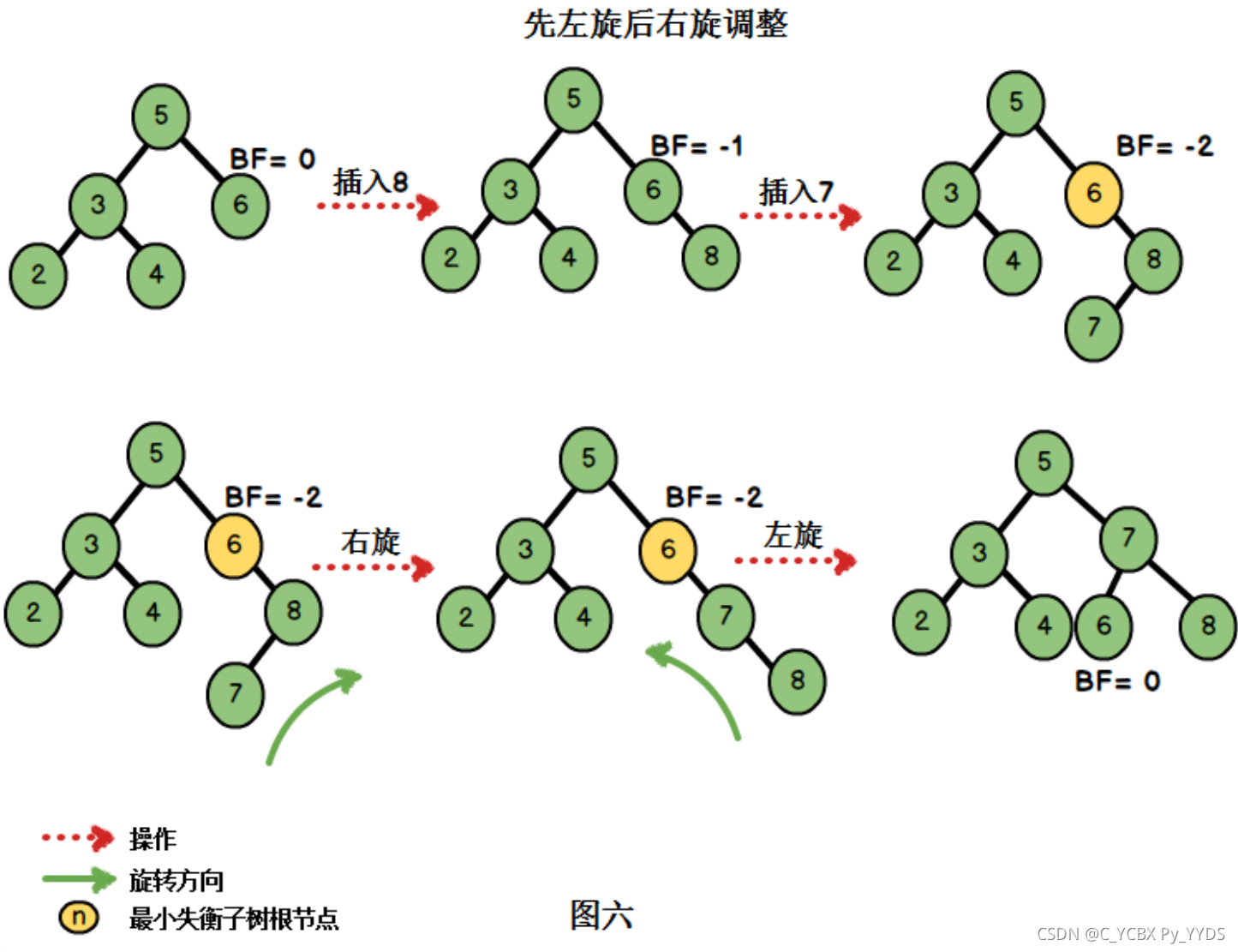 这种情况,总结起来就是“在右子树上插入左孩子导致AVL树失衡",此时我们需要进行先右旋后左旋的调整。
调整的代码为:
这种情况,总结起来就是“在右子树上插入左孩子导致AVL树失衡",此时我们需要进行先右旋后左旋的调整。
调整的代码为:
static node *rotateLeftRight(node *root) {
root->lchild = rotateLeft(root->lchild);
return rotateRight(root);
}
结合例子进行分析:
- 首先对最小不平衡子树的根节点(也就是节点6)的右孩子(也就是8)进行右旋操作
- 再对节点6进行一次左旋操作
情况四:先右旋再左旋
根据对称性原理,当我们“在左子树上插入右孩子导致AVL树失衡",此时我们需要进行先左旋后右旋的调整。如果你不理解接着看图。
我们接着插入节点{0,1}

调整的代码:
static node *rotateRightLeft(node *root) {
root->rchild = rotateRight(root->rchild);
return rotateLeft(root);
}
结合例子进行分析:
- 首先对最小不平衡子树的根节点(也就是节点2)的左孩子(也就是0)进行左旋操作
- 再对节点2进行一次右旋操作
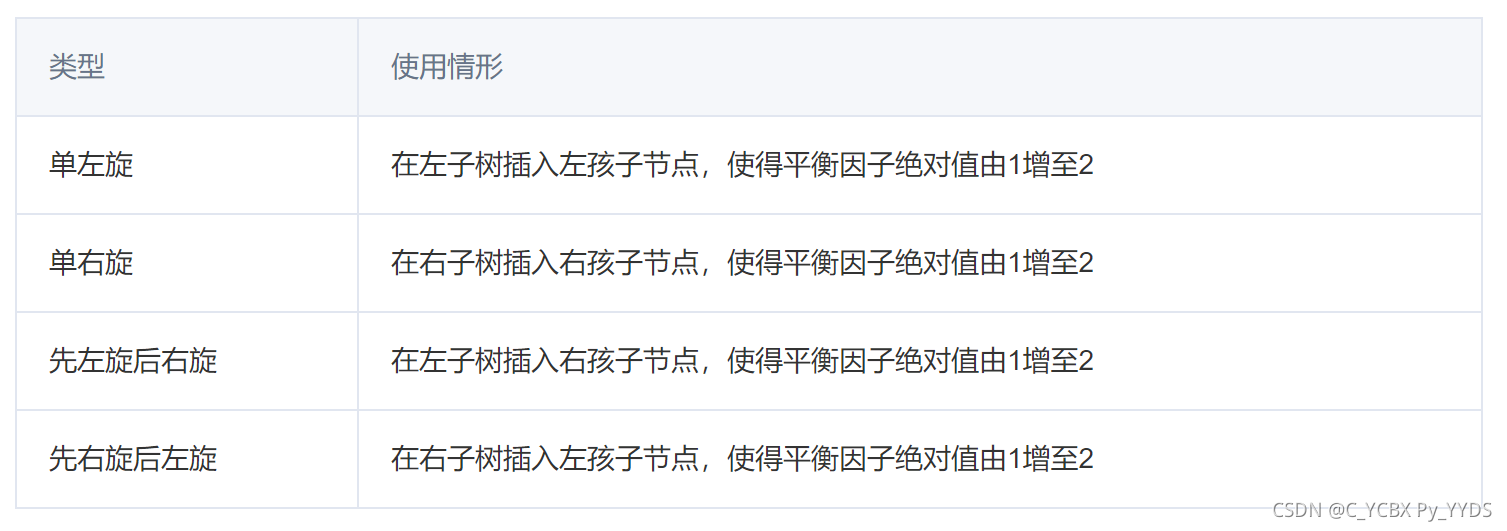
总结:四种失衡调整
7. 插入新结点
//需要是否兼容相等的元素,可通过对 x<root->val 或 x>root->val 这两个中的一个取等号即可
static node *Insert(int x, node *root, int& size) { //所有的deep的更新都在后序遍历后
if (root == nullptr) {
root = new node(x);
size++;//创建结点后size++
} else if (x < root->val) {
root->lchild = Insert(x, root->lchild, size);
//由于在更新该root结点之前,当平衡度未达到该要求之前肯定以及是进行了update_depth操作
if (get_depth(root->lchild) - get_depth(root->rchild) == 2)
root = x < root->lchild->val ? rotateRight(root) : rotateLeftRight(root);
} else if (x > root->val) {
root->rchild = Insert(x, root->rchild, size);
if (get_depth(root->lchild) - get_depth(root->rchild) == -2)
root = x > root->rchild->val ? rotateLeft(root) : rotateRightLeft(root);
}
update_depth(root);
return root;
}
8. 删除结点
失衡的处理: 删除节点也可能导致AVL树的失衡,实际上删除节点和插入节点是一种互逆的操作:
- 删除右子树的节点导致AVL树失衡时,相当于在左子树插入节点导致AVL树失衡,即情况情况二或情况四。
- 删除左子树的节点导致AVL树失衡时,相当于在右子树插入节点导致AVL树失衡,即情况情况一或情况三。
维持排序树的处理: 另外,AVL树也是一棵二叉排序树,因此在删除节点时也要维护二叉排序树的性质。
- 如果删除结点为叶子结点,则直接删除,并不会改变搜索树的性质。
- 如果删除结点只有左子树或者右子树,则直接把要删除的结点的数据用下一个结点覆盖,然后删除下一个结点,由于复制了下一层的左右孩子指针,所以不会出现断层的。
- 如果删除结点左右子树都有,则找出该节点的前驱结点或后继结点的值进行覆盖(不覆盖指针,这样便仍然是排序二叉树了,然后**继续递归寻找对应的前驱或者后继结点进行删除,**因为左右子树都有,所以它们的前驱或者后继只能是叶子结点,找到直接删除即可。
删除处理代码:
我这里对删除操作进行了进一步优化,如果被删除结点的左右子树都存在,则查看左右子树的高度,如果左边高于右边则选择前驱结点进行删除,反之则后继。
static node *remove(int x, node *root, int& size) {
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
if (x == root->val) {
/*左右子树均不为空---用中序的前驱或者后继来进行替换*/
if (root->lchild != nullptr && root->rchild != nullptr) {
/*根据左右子树的深度来选择删除替换哪边的*/
if (get_depth(root->lchild) > get_depth(root->rchild)) {
node* t = getMaxNode(root->lchild);
root->val = t->val;
root->lchild = remove(t->val, root->lchild, size);
} else {
node* t = getMinNode(root->rchild);
root->val = t->val;
root->rchild = remove(t->val, root->rchild, size);
}
}
/*左右子树至少有一个为空的情况,直接往下走一步即可*/
else {
node* tmp = root->lchild == nullptr ? root->rchild : nullptr;
if (tmp != nullptr) {
*root = *tmp;
delete tmp;
}
else {
delete root;
root = nullptr;
}
//删除时size--
size--;
}
} else if (x < root->val) {
root->lchild = remove(x, root->lchild, size);
if (get_depth(root->lchild) - get_depth(root->rchild) == -2)
root = get_depth(root->rchild->lchild) > get_depth(root->rchild->rchild) ? rotateRightLeft(root) : rotateLeft(root);
} else {
root->rchild = remove(x, root->rchild, size);
if (get_depth(root->lchild) - get_depth(root->rchild) == 2)
root = get_depth(root->lchild->rchild) > get_depth(root->lchild->lchild) ? rotateLeftRight(root) : rotateRight(root);
}
return root;
}
9. 查找元素
二叉树是一种递归的定义,因此,二叉树的许多操作都可以通过递归简单地实现,例如遍历二叉树、查找指定元素、销毁二叉树等。
这里使用了迭代方式。
bool find(int x) {
//查找直接迭代方式即可
node *f = head;
while (f != nullptr) {
if (x == f->val)
return true;
else if (x < f->val)
f = f->lchild;
else
f = f->rchild;
}
return false;
}
10. 遍历二叉树
- 我这里只提供了中序遍历的打印,方便验证二叉搜索树的情况。
static void inorder(node *root) {
if (root != nullptr) {
inorder(root->lchild);
printf("%d ", root->val);
inorder(root->rchild);
}
}
11. AVL树的销毁
直接利用后序先处理完左右子树再处理根节点。
static void destroy(node *root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return;
destroy(root->lchild);
destroy(root->rchild);
delete root;
root = nullptr;
}
12. 迭代器的设计
- 关于C++里面的迭代器,其实就是方便遍历容器中的元素,而迭代器需要模拟指针的行为,所以在C++中迭代器其实就是对指针特别包装的类,对其进行一些运算符的重载即可。
内部类充当迭代器
由于需要满足顺序容器的迭代顺序,所以++和--操作对应后继和前驱。
/*iterator part*/
class iterator { //封装迭代器
node* head;
node* root;
public:
iterator(node* head, node* root): head(head), root(root) {}
iterator& operator++() { //直接把root加为当前的后继结点
root = getNext(head, root);
return *this;
}
bool operator==(const iterator& x) {
return this->root == x.root;
}
bool operator!=(const iterator& x) {
return this->root != x.root;
}
iterator operator++(int) {
iterator t = *this;
root = getNext(head, root);
return t;
}
iterator& operator--() { //直接把root赋值为前驱结点
root = getPre(head, root);
return *this;
}
iterator operator--(int) {
iterator t = *this;
root = getPre(head, root);
return t;
}
node& operator*() { //解引用的重载
return *root;
}
};
外部类提供外界begin()和end()接口得到迭代器的始端和末端
iterator begin() {
node* min = getMinNode(head);
return iterator(head, min);
}
iterator end() { //end表示结束标记
return iterator(head, nullptr);
}
完整代码
AVLTree.h
//
// Created by Alone on 2021/10/12.
//
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cassert>
#ifndef MY_TINY_STL_AVLTREE_H
#define MY_TINY_STL_AVLTREE_H
namespace L_B__ {
struct node {
int val;
int depth;
node *lchild;
node *rchild;
node() : val(0), lchild(nullptr), rchild(nullptr) {}
node(int x) : val(x), lchild(nullptr), rchild(nullptr) {}
};
class AVLTree {
/*date part*/
node *head;
int length;
public:
/*construct and destruct part*/
AVLTree() : head(nullptr), length(0) {}
AVLTree(int x) : head(new node(x)), length(1) {}
~AVLTree() {
destroy(head);
}
public:
/*iterator part*/
class iterator {//封装迭代器:内部类--只能调用外部类的静态函数
node *head;
node *root;
public:
iterator(node *head, node *root) : head(head), root(root) {}
iterator &operator++();
bool operator==(const iterator &x);
bool operator!=(const iterator &x);
iterator operator++(int);
iterator &operator--();
iterator operator--(int);
int operator*();
};
private:
/*static member function*/
/*Rotate Part*/
static node *rotateRight(node *root);
static node *rotateLeft(node *root);
static node *rotateLeftRight(node *root);
static node *rotateRightLeft(node *root);
/*Destruct*/
static void destroy(node *root);
/*Getter*/
static node *getNext(node *root, node *p);
static node *getPre(node *root, node *p);
static node *getMinNode(node *root);
static node *getMaxNode(node *root);
static int get_depth(node *root);
static void update_depth(node *root);
/*Insert&Remove*/
static node *Insert(int x, node *root, int &size);
static node *remove(int x, node *root, int &size);
/*print_order*/
static void inorder(node *root);
public:
/*public interface*/
/*clear&empty*/
void clear();
bool isEmpty();
/*find*/
bool find(int x);
/*insert&remove*/
void insert(int x);
void remove(int x);
/*size*/
int size();
/*begin&end*/
iterator begin();
iterator end();
/*print*/
void inorder_print();
};
}
#endif //MY_TINY_STL_AVLTREE_H
AVLTree.cpp
//
// Created by Alone on 2021/10/12.
//
#include "AVLTree.h"
/*Rotate*/
L_B__::node *L_B__::AVLTree::rotateRight(L_B__::node *root) {//右旋
node *son = root->lchild;
root->lchild = son->rchild;
son->rchild = root;
update_depth(root);//更新深度(右旋只会对这两结点产生影响
update_depth(son);
return son;
}
L_B__::node *L_B__::AVLTree::rotateLeft(L_B__::node *root) {
node *son = root->rchild;
root->rchild = son->lchild;
son->lchild = root;
update_depth(root);
update_depth(son);
return son;
}
L_B__::node *L_B__::AVLTree::rotateLeftRight(L_B__::node *root) {
root->lchild = rotateLeft(root->lchild);
return rotateRight(root);
}
L_B__::node *L_B__::AVLTree::rotateRightLeft(L_B__::node *root) {
root->rchild = rotateRight(root->rchild);
return rotateLeft(root);
}
/*Destruct*/
void L_B__::AVLTree::destroy(L_B__::node *root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return;
destroy(root->lchild);
destroy(root->rchild);
delete root;
root = nullptr;
}
/*Getter*/
L_B__::node *L_B__::AVLTree::getNext(L_B__::node *root, L_B__::node *p) {
if (root == nullptr || p == nullptr) return nullptr;
if (p->val >= root->val) {
return getNext(root->rchild, p);
} else {
node *left = getNext(root->lchild, p);
return left ? left : root;
}
}
L_B__::node *L_B__::AVLTree::getPre(L_B__::node *root, L_B__::node *p) {
if (root == nullptr || p == nullptr)return nullptr;
if (p->val <= root->val) {
return getPre(root->lchild, p);
} else {
node *right = getPre(root->rchild, p);
return right ? right : root;
}
}
L_B__::node *L_B__::AVLTree::getMinNode(L_B__::node *root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
while (root->lchild != nullptr)
root = root->lchild;
return root;
}
L_B__::node *L_B__::AVLTree::getMaxNode(L_B__::node *root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
while (root->rchild != nullptr)
root = root->rchild;
return root;
}
int L_B__::AVLTree::get_depth(L_B__::node *root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
return root->depth;
}
void L_B__::AVLTree::update_depth(L_B__::node *root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return;
root->depth = std::max(get_depth(root->lchild), get_depth(root->rchild)) + 1;
}
/*Insert&remove*/
L_B__::node *L_B__::AVLTree::Insert(int x, L_B__::node *root, int &size) {
if (root == nullptr) {
root = new node(x);
size++;//创建结点后size++
} else if (x < root->val) {
root->lchild = Insert(x, root->lchild, size);
//由于在更新该root结点之前,当平衡度未达到该要求之前肯定以及是进行了update_depth操作
if (get_depth(root->lchild) - get_depth(root->rchild) == 2)
root = x < root->lchild->val ? rotateRight(root) : rotateLeftRight(root);
} else if (x > root->val) {
root->rchild = Insert(x, root->rchild, size);
if (get_depth(root->lchild) - get_depth(root->rchild) == -2)
root = x > root->rchild->val ? rotateLeft(root) : rotateRightLeft(root);
}
update_depth(root);
return root;
}
L_B__::node *L_B__::AVLTree::remove(int x, L_B__::node *root, int &size) {
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
if (x == root->val) {
/*左右子树均不为空---用中序的前驱或者后继来进行替换*/
if (root->lchild != nullptr && root->rchild != nullptr) {
/*根据左右子树的深度来选择删除替换哪边的*/
if (get_depth(root->lchild) > get_depth(root->rchild)) {
node *t = getMaxNode(root->lchild);
root->val = t->val;
root->lchild = remove(t->val, root->lchild, size);
} else {
node *t = getMinNode(root->rchild);
root->val = t->val;
root->rchild = remove(t->val, root->rchild, size);
}
}
/*左右子树至少有一个为空的情况,直接往下走一步即可*/
else {
node *tmp = root->lchild == nullptr ? root->rchild : nullptr;
if (tmp != nullptr) {
*root = *tmp;
delete tmp;
} else {
delete root;
root = nullptr;
}
//删除时size--
size--;
}
} else if (x < root->val) {
root->lchild = remove(x, root->lchild, size);
if (get_depth(root->lchild) - get_depth(root->rchild) == -2)
root = get_depth(root->rchild->lchild) > get_depth(root->rchild->rchild) ? rotateRightLeft(root)
: rotateLeft(root);
} else {
root->rchild = remove(x, root->rchild, size);
if (get_depth(root->lchild) - get_depth(root->rchild) == 2)
root = get_depth(root->lchild->rchild) > get_depth(root->lchild->lchild) ? rotateLeftRight(root)
: rotateRight(root);
}
return root;
}
/*print part*/
void L_B__::AVLTree::inorder(L_B__::node *root) {
if (root != nullptr) {
inorder(root->lchild);
printf("%d ", root->val);
inorder(root->rchild);
}
}
/*clear&isEmpty*/
void L_B__::AVLTree::clear() {
destroy(head);
}
bool L_B__::AVLTree::isEmpty() {
return head == nullptr;
}
/*find*/
bool L_B__::AVLTree::find(int x) {
//查找直接迭代方式即可
node *f = head;
while (f != nullptr) {
if (x == f->val)
return true;
else if (x < f->val)
f = f->lchild;
else
f = f->rchild;
}
return false;
}
/*insert&remove*/
void L_B__::AVLTree::insert(int x) {
head = Insert(x, head, length);
}
void L_B__::AVLTree::remove(int x) {
assert(length != 0);
head = remove(x, head, length);
}
int L_B__::AVLTree::size() {
return length;
}
/*begin&end*/
L_B__::AVLTree::iterator L_B__::AVLTree::begin() {
node *min = getMinNode(head);
return iterator(head, min);
}
L_B__::AVLTree::iterator L_B__::AVLTree::end() {
return iterator(head, nullptr);
}
/*print*/
void L_B__::AVLTree::inorder_print() {
printf("Inorder:# ");
inorder(head);
}
/*iterator implement*/
bool L_B__::AVLTree::iterator::operator==(const L_B__::AVLTree::iterator &x) {
return this->root == x.root;
}
bool L_B__::AVLTree::iterator::operator!=(const L_B__::AVLTree::iterator &x) {
return this->root != x.root;
}
L_B__::AVLTree::iterator L_B__::AVLTree::iterator::operator++(int) {
iterator t = *this;
root = getNext(head, root);
return t;
}
L_B__::AVLTree::iterator &L_B__::AVLTree::iterator::operator--() {
root = getPre(head, root);
return *this;
}
L_B__::AVLTree::iterator L_B__::AVLTree::iterator::operator--(int) {
iterator t = *this;
root = getPre(head, root);
return t;
}
int L_B__::AVLTree::iterator::operator*() {
return root->val;
}
L_B__::AVLTree::iterator &L_B__::AVLTree::iterator::operator++() {
root = getNext(head, root);
return *this;
}
测试
- 注意:以下数据由于存在大量相同的值,而我写的这个AVLTree并未对相同的值进行存储,所以节省了大量插入时候的调整时间,所以才能达到不错的插入性能,实际上只要实际插入的数据够多,和红黑树的差距就越大,我之前试过十亿不重复数据插入AVL和RB的测试,AVL运行几分钟,而RB一分钟内解决。但查找和删除方面AVL仍然是吊打RB(毕竟严格平衡树
与STL中的set(红黑树)进行对比:

测试代码
int main() {
using namespace std;
AVLTree x;
set<int>Q;
printf("插入测试\n");
auto start = clock();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000000; ++i) {
x.insert(i%10000000);
}
std::cout<<"AVLTree"<<clock()-start<<"ms"<<std::endl;
start = clock();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000000; ++i) {
Q.insert(i%10000000);
}
std::cout<<"RBTree"<<clock()-start<<"ms"<<std::endl;
printf("迭代测试\n");
start = clock();
for(auto it = x.begin();it!=x.end();++it){
continue;
}
std::cout<<"AVLTree"<<clock()-start<<"ms"<<std::endl;
start = clock();
for(auto it = Q.begin();it!=Q.end();++it){
continue;
}
std::cout<<"RBTree"<<clock()-start<<"ms"<<std::endl;
printf("查找测试\n");
start = clock();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000000; ++i) {
x.find(i);
}
std::cout<<"AVLTree"<<clock()-start<<"ms"<<std::endl;
start = clock();
for(int i = 0;i<100000000;++i){
Q.count(i);
}
std::cout<<"RBTree"<<clock()-start<<"ms"<<std::endl;
printf("删除测试\n");
start = clock();
for(int i=0;i<10000000;i++){
x.remove(i);
}
std::cout<<"AVLTree"<<clock()-start<<"ms"<<"length"<<x.size()<<std::endl;
start = clock();
for(int i=0;i<10000000;i++){
Q.erase(i);
}
std::cout<<"RBTree"<<clock()-start<<"ms"<<"length"<<Q.size()<<std::endl;
return 0;
}
测试总结
通过不断对比红黑树(RB)和AVL,得出以下结论:
- 插入操作红黑树比AVL快很多,数据量越大优势越明显。
- 查找和删除操作红黑树却是比AVL慢很多,同样也是数据量越大越明显。
总的来说,如果所需要管理的数据量很大,并且需要频繁的插入,那么红黑树更适合你,如果只需要插入一次后,对数据进行查找管理,那么AVL更加的适合你!
解题测试
在以上设计的基础上加个get_head方法即可。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
struct node {
int val;
int depth;
node *lchild;
node *rchild;
node() : val(0), lchild(nullptr), rchild(nullptr) {}
node(int x) : val(x), lchild(nullptr), rchild(nullptr) {}
};
class AVLTree {
/*date part*/
node *head;
int size;
public:
/*construct and destruct part*/
AVLTree() : head(nullptr),size(0) {}
AVLTree(int x) : head(new node(x)),size(1) {}
~AVLTree() {
destroy(head);
}
private:
/*static function part*/
static node *rotateRight(node *root) {//右旋
node *son = root->lchild;
root->lchild = son->rchild;
son->rchild = root;
update_depth(root);//更新深度(右旋只会对这两结点产生影响
update_depth(son);
return son;
}
static node *rotateLeft(node *root) {
node *son = root->rchild;
root->rchild = son->lchild;
son->lchild = root;
update_depth(root);
update_depth(son);
return son;
}
static node *rotateLeftRight(node *root) {
root->lchild = rotateLeft(root->lchild);
return rotateRight(root);
}
static node *rotateRightLeft(node *root) {
root->rchild = rotateRight(root->rchild);
return rotateLeft(root);
}
static void destroy(node *root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return;
destroy(root->lchild);
destroy(root->rchild);
delete root;
root = nullptr;
}
static node* getMinNode(node* root){
if(root== nullptr)
return nullptr;
while(root->lchild!= nullptr)
root = root->lchild;
return root;
}
static node* getMaxNode(node* root){
if(root== nullptr)
return nullptr;
while(root->rchild!= nullptr)
root = root->rchild;
return root;
}
static int get_depth(node *root) {//得到深度
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
return root->depth;
}
static void update_depth(node *root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return;
root->depth = std::max(get_depth(root->lchild), get_depth(root->rchild)) + 1;
}
static node *Insert(int x, node *root) {//所有的deep的更新都在后序遍历后
if (root == nullptr) {
root = new node(x);
} else if (x <= root->val) {
root->lchild = Insert(x, root->lchild);
//由于在更新该root结点之前,当平衡度未达到该要求之前肯定以及是进行了update_depth操作
if (get_depth(root->lchild) - get_depth(root->rchild) == 2)
root = x <= root->lchild->val ? rotateRight(root) : rotateLeftRight(root);
} else if (x > root->val) {
root->rchild = Insert(x, root->rchild);
if (get_depth(root->lchild) - get_depth(root->rchild) == -2)
root = x >= root->rchild->val ? rotateLeft(root) : rotateRightLeft(root);
}
update_depth(root);
return root;
}
static node *remove(int x, node *root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
if (x == root->val) {
/*左右子树均不为空---用中序的前驱或者后继来进行替换*/
if (root->lchild != nullptr && root->rchild != nullptr) {
/*根据左右子树的深度来选择删除替换哪边的*/
if(get_depth(root->lchild)>get_depth(root->rchild)){
node* t = getMaxNode(root->lchild);
root->val = t->val;
root->lchild = remove(t->val,root->lchild);
}else{
node* t = getMinNode(root->rchild);
root->val = t->val;
root->rchild = remove(t->val,root->rchild);
}
}
/*左右子树至少有一个为空的情况,直接往下走一步即可*/
else{
node* tmp = root->lchild== nullptr?root->rchild: nullptr;
if(tmp!= nullptr){
*root = *tmp;
delete tmp;
}
else{
delete root;
root = nullptr;
}
}
} else if (x < root->val) {
root->lchild = remove(x, root->lchild);
if(get_depth(root->lchild)-get_depth(root->rchild)==-2)
root = get_depth(root->rchild->lchild)>get_depth(root->rchild->rchild)?rotateRightLeft(root): rotateLeft(root);
} else {
root->rchild = remove(x, root->rchild);
if(get_depth(root->lchild)-get_depth(root->rchild)==2)
root = get_depth(root->lchild->rchild)>get_depth(root->lchild->lchild)?rotateLeftRight(root): rotateRight(root);
}
return root;
}
static void inorder(node *root) {
if (root != nullptr) {
inorder(root->lchild);
printf("%d ", root->val);
inorder(root->rchild);
}
}
public:
/*public function part*/
void insert(int x) {
//递归方式插入,方便后续处理
head = Insert(x, head);
size++;
}
void remove(int x){
assert(size!=0);
head = remove(x,head);
size--;
}
void clear() {
destroy(head);
}
bool isEmpty() {
return head == nullptr;
}
bool find(int x) {
//查找直接迭代方式即可
node *f = head;
while (f != nullptr) {
if (x == f->val)
return true;
else if (x < f->val)
f = f->lchild;
else
f = f->rchild;
}
return false;
}
void inorder_print() {
printf("Inorder:# ");
inorder(head);
}
node* get_head(){
return head;
}
};
int main() {
AVLTree x;
int n;std::cin>>n;
while(n--){
int t;
std::cin>>t;
x.insert(t);
}
printf("%d",x.get_head()->val);
return 0;
}





 京公网安备 11010502036488号
京公网安备 11010502036488号