P1002 [NOIP 2002 普及组] 过河卒
题目描述
棋盘上 点有一个过河卒,需要走到目标
点。卒行走的规则:可以向下、或者向右。同时在棋盘上
点有一个对方的马,该马所在的点和所有跳跃一步可达的点称为对方马的控制点。因此称之为“马拦过河卒”。
棋盘用坐标表示, 点
、
点
,同样马的位置坐标是需要给出的。
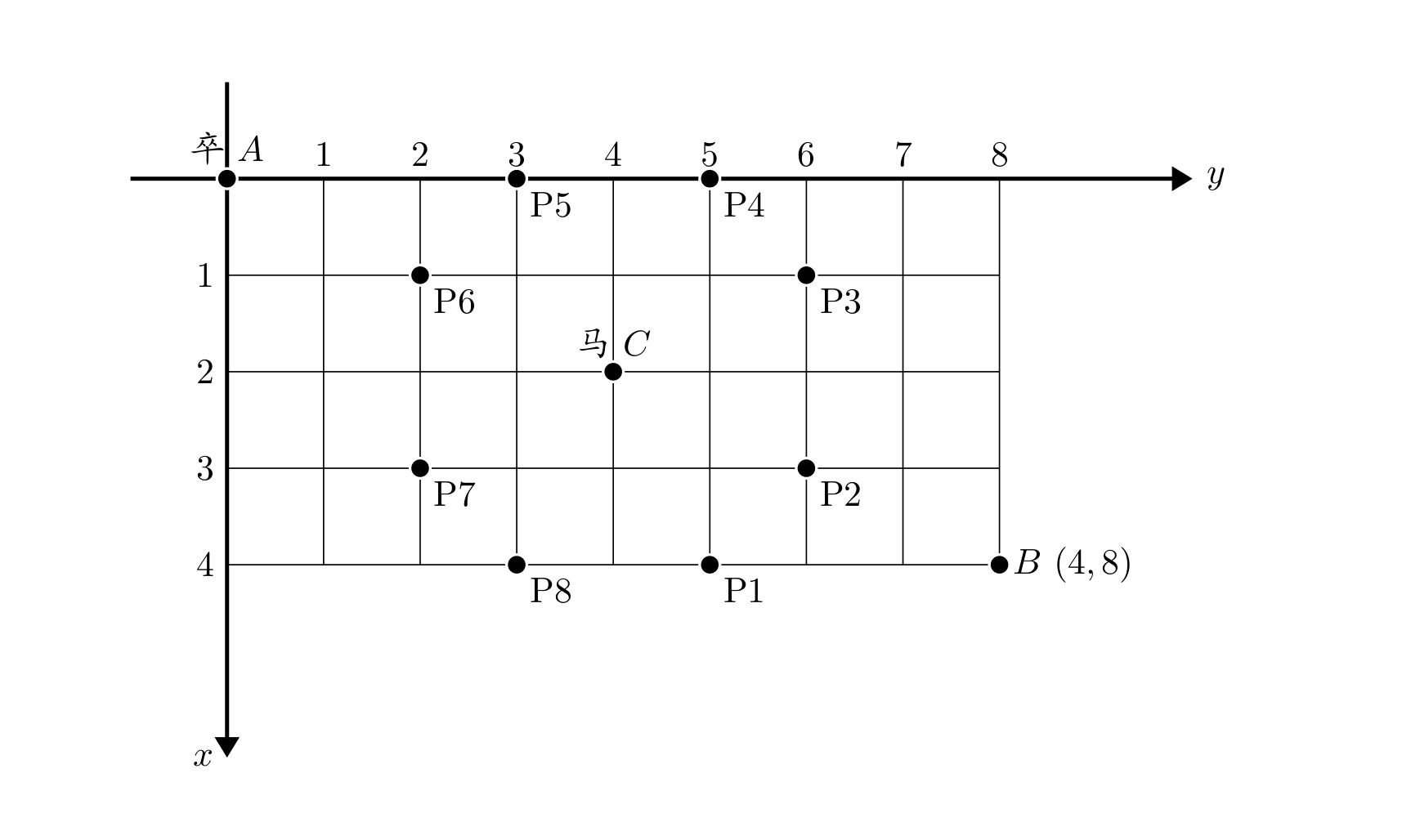
现在要求你计算出卒从 点能够到达
点的路径的条数,假设马的位置是固定不动的,并不是卒走一步马走一步。
输入格式
一行四个正整数,分别表示 点坐标和马的坐标。
输出格式
一个整数,表示所有的路径条数。
输入输出样例 #1
输入 #1
6 6 3 3
输出 #1
6
说明/提示
对于 的数据,
,
马的坐标
。
【题目来源】
NOIP 2002 普及组第四题
AC代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using i64 = long long;
using u64 = unsigned long long;
using u32 = unsigned;
using u128 = unsigned __int128;
#define lowbit(x) = ((x) & -(x))
#define rep_0(a, b, c) for (int a = b; a < c; a++)
#define rep_1(a, b, c) for (int a = b; a <= c; a++)
#define per(a, b, c) for (int a = b; a >= c; a--)
using namespace std;
void solve()
{
const int dir[8][2] = {{1, 2}, {1, -2}, {2, 1}, {2, -1}, {-1, 2}, {-1, -2}, {-2, 1}, {-2, -1}};
bool val[30][30] = {false};
vector<vector<i64>> ans(31, vector<i64>(31, 0));
int x, y, mx, my;
cin >> x >> y >> mx >> my;
val[mx][my] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
int nx = mx + dir[i][0];
int ny = my + dir[i][1];
if (nx >= 0 && nx <= x && ny >= 0 && ny <= y)
{
val[nx][ny] = true;
}
}
ans[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i <= x; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j <= y; j++)
{
if (val[i][j] == false)
{
if (i)
{
ans[i][j] += ans[i - 1][j];
}
if (j)
{
ans[i][j] += ans[i][j - 1];
}
}
}
}
cout << ans[x][y] << endl;
return;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int t = 1;
// cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}




 京公网安备 11010502036488号
京公网安备 11010502036488号