2022-01-25:序列化和反序列化 N 叉树。 序列化是指将一个数据结构转化为位序列的过程,因此可以将其存储在文件中或内存缓冲区中,以便稍后在相同或不同的计算机环境中恢复结构。 设计一个序列化和反序列化 N 叉树的算法。 一个 N 叉树是指每个节点都有不超过 N 个孩子节点的有根树。 序列化 / 反序列化算法的算法实现没有限制。 你只需要保证 N 叉树可以被序列化为一个字符串并且该字符串可以被反序列化成原树结构即可。 注意: N 的范围在 [1, 1000] 不要使用类成员 / 全局变量 / 静态变量来存储状态。 你的序列化和反序列化算法应是无状态的。 力扣428。
答案2022-01-25:
自然智慧。递归。
代码用golang编写。代码如下:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strconv"
"strings"
)
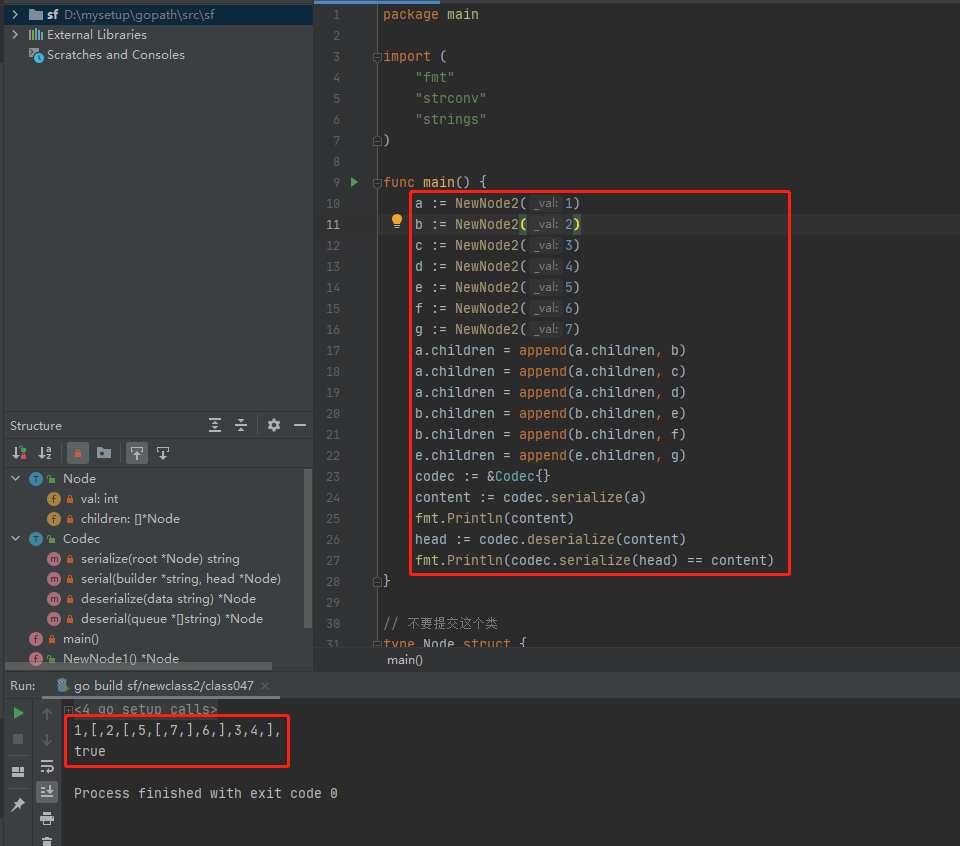
func main() {
a := NewNode2(1)
b := NewNode2(2)
c := NewNode2(3)
d := NewNode2(4)
e := NewNode2(5)
f := NewNode2(6)
g := NewNode2(7)
a.children = append(a.children, b)
a.children = append(a.children, c)
a.children = append(a.children, d)
b.children = append(b.children, e)
b.children = append(b.children, f)
e.children = append(e.children, g)
codec := &Codec{}
content := codec.serialize(a)
fmt.Println(content)
head := codec.deserialize(content)
fmt.Println(codec.serialize(head) == content)
}
// 不要提交这个类
type Node struct {
val int
children []*Node
}
func NewNode1() *Node {
ret := &Node{}
ret.children = make([]*Node, 0)
return ret
}
func NewNode2(_val int) *Node {
ret := &Node{}
ret.val = _val
ret.children = make([]*Node, 0)
return ret
}
func NewNode3(_val int, _children []*Node) *Node {
ret := &Node{}
ret.val = _val
ret.children = _children
return ret
}
// 提交下面这个类
type Codec struct {
}
func (this *Codec) serialize(root *Node) string {
if root == nil { // 空树!直接返回#
return "#"
}
builder := ""
this.serial(&builder, root)
return builder
}
// 当前来到head
func (this *Codec) serial(builder *string, head *Node) {
*builder += fmt.Sprint(head.val) + ","
if len(head.children) > 0 {
*builder += "[,"
for _, next := range head.children {
this.serial(builder, next)
}
*builder += "],"
}
}
func (this *Codec) deserialize(data string) *Node {
if data == "#" {
return nil
}
splits := strings.Split(data, ",")
queue := make([]string, 0)
for _, str := range splits {
queue = append(queue, str)
}
return this.deserial(&queue)
}
func (this *Codec) deserial(queue *[]string) *Node {
v, _ := strconv.Atoi((*queue)[0])
cur := NewNode2(v)
*queue = (*queue)[1:]
cur.children = make([]*Node, 0)
if len(*queue) > 0 && (*queue)[0] == "[" {
*queue = (*queue)[1:]
for (*queue)[0] != "]" {
child := this.deserial(queue)
cur.children = append(cur.children, child)
}
*queue = (*queue)[1:]
}
return cur
}
执行结果如下:






 京公网安备 11010502036488号
京公网安备 11010502036488号