1. 二维向量
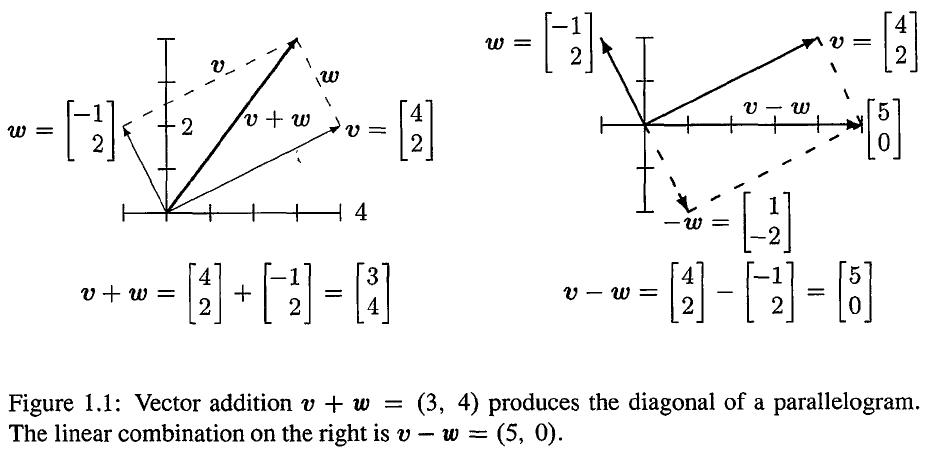
在二维平面中,一个二维向量可以用一个箭头来表示,这个箭头起始于原点,终点坐标 (x,y) 分别为向量中的两个元素,而 cv 与 dw 的和则是向量 v 和 w的线性组合。
2. 三维向量
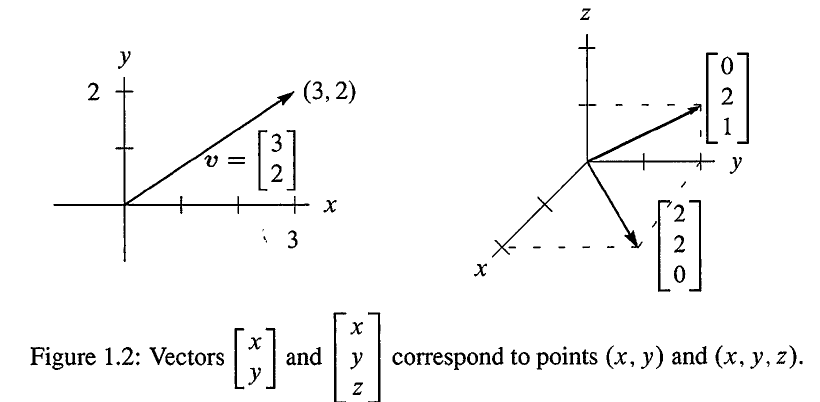
三维向量和二维向量类似,可以表示为三维平面中的一个箭头,只不过坐标变成了 (x,y,z)。
针对三维向量 u, v 和 w,有
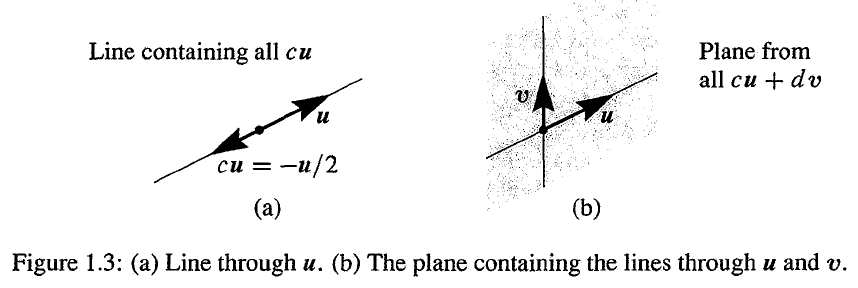
- 所有 cu 的组合会填满一条直线
- 所有 cu+dv 的组合会填满一个平面,如果 u 和 v 不在一条直线上
- 所有 cu+dv+ew 的组合会填满三维空间,如果 w 不在 u 和 v 组合成的平面上
3. 长度和点积
两个向量 v=(v1,v2) 和 w=(w1,w2) 的点积或者内积 v⋅w 定义为:
v⋅w=v1w1+v2w2
如果两个的向量的点积为零,说明这两个向量是垂直的,它们之间的角度为 90°。
另一个重要的情况是一个向量和自己点积,这时候点积的结果就是向量长度的平方,或者说向量的长度就等于与自身点积的平方根。
Length=norm(v)=∣∣v∣∣=v⋅v
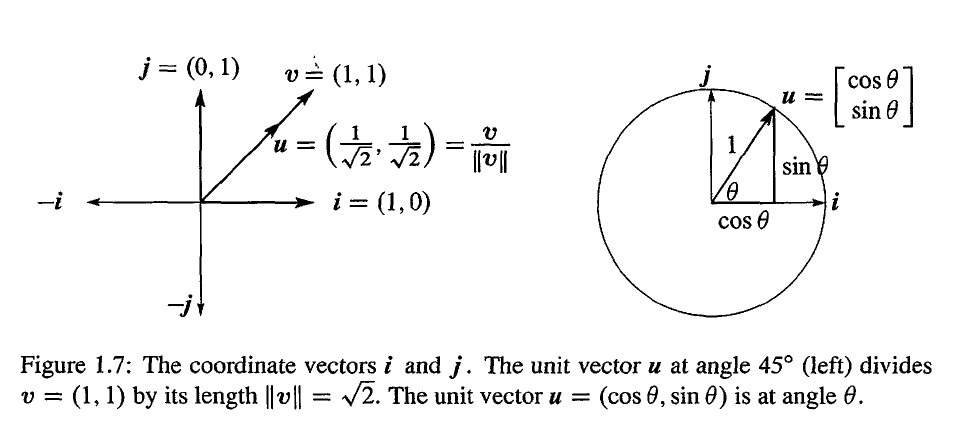
单位向量就是向量长度为 1 的向量,也就是 u⋅u=1。 u=v/∣∣v∣∣ 是一个和 v 在一个方向上的单位向量。
沿着 x 轴和 y 轴 的单位向量称为 i 和 j,在 xy 平面中,单位向量 u 和 x 轴构成一个夹角 θ 。
i=[10],j=[01],u=[cosθsinθ]
当两个向量之间的角度小于 90° 时,它们的点积大于 0;当两个向量之间的角度大于 90° 时,它们的点积小于 0;而当两个向量之间的角度等于 90° 时,它们的点积等于 0。
我们可以直观地看到这种情况,当这两个向量分别为单位向量 u=(cosθ,sinθ) 和 i=(1,0) 时,这时候 u⋅i=cosθ, θ 也就是这两个向量之间的角度。
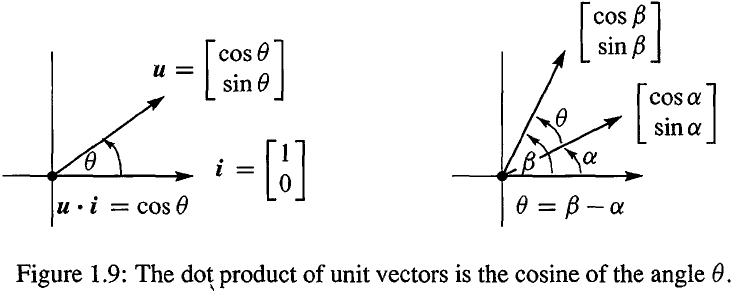
当这两个向量分别旋转到 u=(cosβ,sinβ) 到 i=(cosα,sinα) 时,它们的点积为:
u⋅i=cosβcosα+sinβsinα=cos(β−α)=cosθ
当两个向量不是单位向量的时候,我们就可以先除以向量的长度把它们变成单位向量,因此,同样地,就有:
∣∣v∣∣ ∣∣w∣∣v⋅w=cosθ
因为 ∣cosθ∣不会超过 1,因此我们就得到了 施瓦茨不等式(Schwarz Inequality) 和 三角不等式(Triangle inequality):
∣v⋅w∣⩽∣∣v∣∣ ∣∣w∣∣
∣∣v+w∣∣⩽∣∣v∣∣+∣∣w∣∣
4. 矩阵
给出三个向量
u=⎣⎡1−10⎦⎤,v=⎣⎡01−1⎦⎤,w=⎣⎡001⎦⎤
它们的线性组合 cu+dv+ew 为:
c⎣⎡1−10⎦⎤+d⎣⎡01−1⎦⎤+e⎣⎡001⎦⎤=⎣⎡cd−ce−d⎦⎤
我们将 u,v,w 作为矩阵 A 的列,然后上式可以重写为:
⎣⎡1−1001−1001⎦⎤⎣⎡cde⎦⎤=⎣⎡cd−ce−d⎦⎤
将 c,d,e 换成 x1,x2,x3,我们可以得到:
Ax=⎣⎡uvw⎦⎤⎣⎡x1x2x3⎦⎤=x1u+x2v+x3w=⎣⎡x1x2−x1x3−x2⎦⎤
这就是说, Ax 的结果就是对矩阵 A 的列的线性组合。
我们还可以将上面的乘积表示成另外一种形式,矩阵的行和向量的点积:
Ax=⎣⎡1−1001−1001⎦⎤⎣⎡x1x2x3⎦⎤=⎣⎡(1,0,0)⋅(x1,x2,x3)(−1,1,0)⋅(x1,x2,x3)(0,−1,1)⋅(x1,x2,x3)⎦⎤
获取更多精彩,请关注「seniusen」!











 京公网安备 11010502036488号
京公网安备 11010502036488号