1. 消元的思想
针对下面的方程,我们无法直接得到方程的解。
3x − x + 22y = 1y = 11
但如果我们将第二个方程减去第一个方程的 3 倍,上面的方程组就变成了下面这样。
x − 28y = 1y = 8
这时候,我们就可以直接得到 y=1,进而从第一个方程得到 x=3。
可以看到,消元之后,方程组变成了一个下三角(upper triangular)的形式,然后我们就可以用回带法(back substitution)来快速地解出方程组的解。
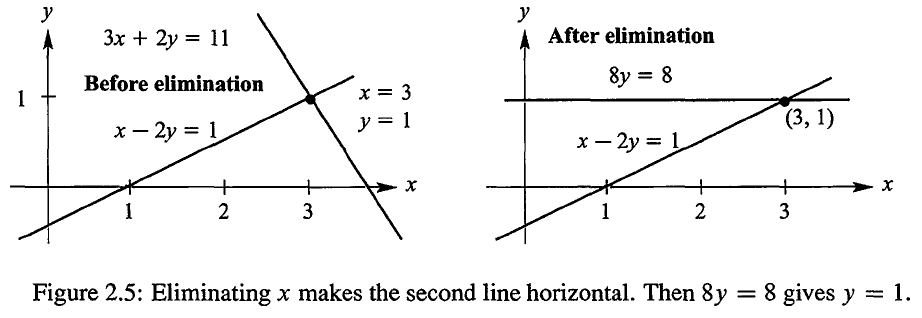
进行消元的那一行的第一个非零值称为主元(pivot),消元时候的乘数就等于待消项的系数除以主元,在上面的例子中,乘数 3=3/1。一般地,乘数可以表示为
lij=第 j 行的主元第 i 行待消去项的系数
43x − x + 82y = 4y = 11
如果我们改变了第一个方程,那么乘数就等于 3/4。消元之后,所有的主元都位于下三角的对角线上,并且主元不能是 0。
4x − 88y = 4y = 8
2. 消元的失效
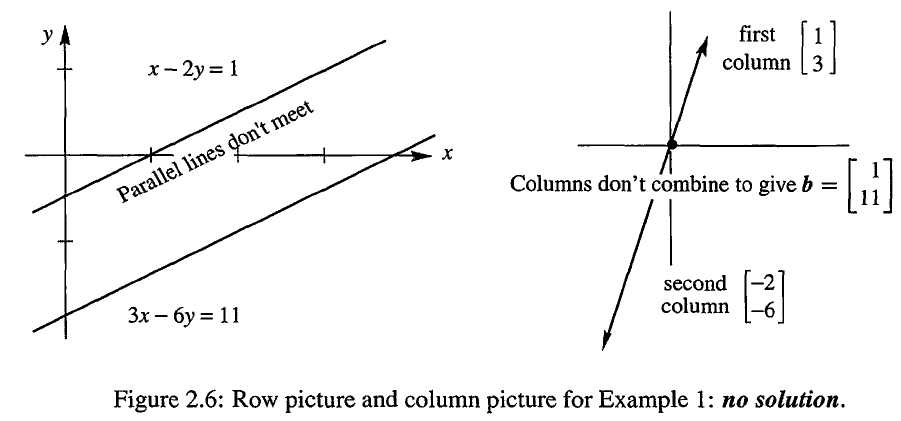
- 无解
3x − x − 26y = 1y = 11消元后x − 20y = 1y = 8
这种情况下,我们遇到了 0y=8,说明原方程组无解。从行图像中,我们也可以看到,两条平行的直线无法相交于一点。而在列图像中,两个在同一方向上的向量不可能线性组合出不在这个方向上的向量。
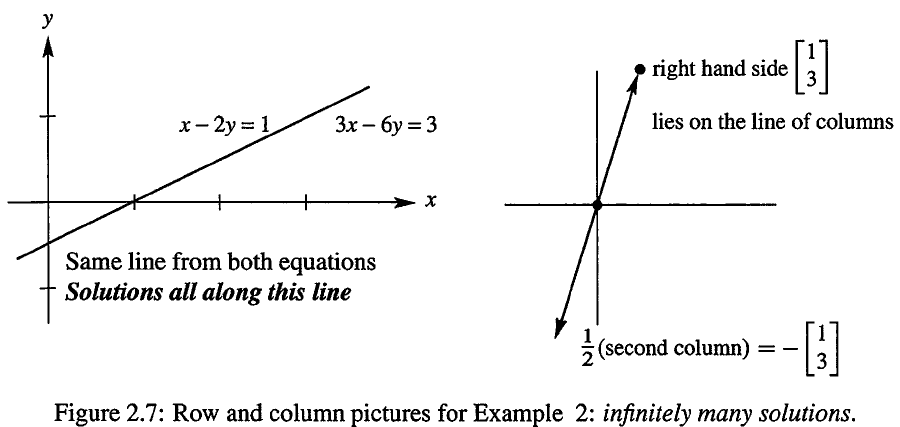
- 无穷解
3x − x − 26y = 1y = 3消元后x − 20y = 1y = 0
这种情况下,我们遇到了 0y=0,任何的 y 值都满足要求,此时 y 是“自由”的,确定了 y 之后 x 则由第一个方程确定。
从行图像中,我们也可以看到,两条直线相同,因此整条直线都是交点。而在列图像中,左边的两个向量和右边的向量方向都相同,有无穷多个线性组合都可以产生右边的向量。
对于有 n 个方程的方程组,如果我们得不到 n 个主元,那么消元就会导致 0̸=0,无解 或者 0=0,无穷解 ,只有正好有 n 个主元的时候,方程组才有解,但我们可能需要进行方程的交换。
03x + x − 22y = 4y = 5消元后3x − 22y = 5y = 4
一开始,第一行的主元为 0,行交换后,我们得到了两个主元 3 和 2,然后,方程就有了正常的解。
3. 三个未知数
24−2x + x + x − 493y − y − y + 237z= 2z= 8z= 10
第一步,方程 2 减去 2 倍的方程 1,得到 y+z=4。
第二步,方程 3 减去 -1 倍的方程 1,得到 y+5z=12。
第一步,方程 3 减去 1 倍的方程 2,得到 4z=8。
2x + 41y − y + 214z= 2z= 8z= 8
三个主元分别为 2, 1, 4,然后我们就可以用回带法求出方程组的解。
4. 用矩阵的形式来消元
24−2x1 + x1 + x1 − 493x2 − x2 − x2 + 237x3= 2x3= 8x3= 10↔⎣⎡24−249−3−2−37⎦⎤⎣⎡x1x2x3⎦⎤=⎣⎡2810⎦⎤
对方程的两边同时进行一步消元,第 2 个方程减去第 1 个方程的 2 倍,我们可以得到:
⎣⎡20−241−3−217⎦⎤⎣⎡x1x2x3⎦⎤=⎣⎡2410⎦⎤
相当于左右两边都乘以了一个矩阵 E21
E21=⎣⎡1−20010001⎦⎤
E21=⎣⎡1−20010001⎦⎤∗⎣⎡row1row2row3⎦⎤=⎣⎡row1row2−2row1row3⎦⎤
E21 称为初等矩阵(elementary matrix)或者消元矩阵(elimination matrix),它可以很简单地从单位矩阵演化而来, Eij 就是将单位矩阵 (i,j) 位置的 0 换成消元过程的乘数 −lij。
I=⎣⎡100010001⎦⎤→E21=⎣⎡1−20010001⎦⎤
获取更多精彩,请关注「seniusen」!









 京公网安备 11010502036488号
京公网安备 11010502036488号