今日小结:今天还是主要做的树链剖分和线段树的题目,巩固了一下,最近没有什么特别想学的知识点,明天准备复习一下二分图的有关知识。
一. 完成的题目:
洛谷P1607,洛谷P3128,SP375,CF438D,洛谷P3398,洛谷P2146
二.
1.当日完成题目数:6道。
2. 未完成6个题目的原因:
3. 复习的知识点:树链剖分,线段树,LCA。
4.不会题目:洛谷P3313
三:
1. 洛谷P1607 [USACO09FEB]庙会班车Fair Shuttle
题目描述
逛逛集市,兑兑奖品,看看节目对农夫约翰来说不算什么,可是他的奶牛们非常缺乏锻炼——如果要逛完一整天的集市,他们一定会筋疲力尽的。所以为了让奶牛们也能愉快地逛集市,约翰准备让奶牛们在集市上以车代步。但是,约翰木有钱,他租来的班车只能在集市上沿直线跑一次,而且只能停靠\(N(1 ≤N≤20000)\)个地点(所有地点都以\(1\)到\(N\)之间的一个数字来表示)。现在奶牛们分成\(K(1≤K≤50000)\)个小组,第i 组有\(M_i(1 ≤M_i≤N)\)头奶牛,他们希望从\(S_i\)跑到\(T_i(1 ≤S_i<T_i≤N)\)。
由于班车容量有限,可能载不下所有想乘车的奶牛们,此时也允许小里的一部分奶牛分开乘坐班车。约翰经过调查得知班车的容量是\(C(1≤C≤100)\),请你帮助约翰计划一个尽可能满足更多奶牛愿望的方案。
输入输出格式
输入格式:
【输入】
第一行:包括三个整数:\(K\),\(N\)和\(C\),彼此用空格隔开。
第二行到\(K+1\)行:在第\(i+1\)行,将会告诉你第\(i\)组奶牛的信息:\(S_i\),\(E_i\)和\(M_i\),彼
此用空格隔开。
输出格式:
【输出】
第一行:可以坐班车的奶牛的最大头数。
输入输出样例
输入样例#1:
8 15 3
1 5 2
13 14 1
5 8 3
8 14 2
14 15 1
9 12 1
12 15 2
4 6 1输出样例#1:
10说明
【样例说明】
班车可以把\(2\)头奶牛从\(1\)送到\(5\),\(3\)头奶牛从\(5\)送到\(8\),\(2\)头奶牛从\(8\)送到\(14\),\(1\)头奶牛从\(9\)送到\(12\),\(1\)头奶牛从\(13\)送到\(14\),\(1\)头奶牛从\(14\)送到\(15\)。
思路:
题意是给你几堆奶牛,每个奶牛都有想去的地方,给你一个汽车,汽车有一个容量和固定的行走路线,询问最多能搭载的奶牛的数量。
我们来考虑一种贪心的思想,按右端点从小到大排一遍序,为什么呢?后面说,然后对排好序的每堆奶牛依次进行遍历,如果当前有空位,空位大于这堆奶牛的数量,那就全上去,不然的话,就能上去几个就上去几个。这样下来的话,结果一定是最优的,其正确性不难证明,因为刚开始我们对每堆奶牛要到的地方从小到大排了序(即终点),那么每个位置最多只有一次奶牛上车,而且这些奶牛来自同一群,所以我们对每堆奶牛分别进行考虑即可,这就是为什么要按右端点排序的原因。贪心过程中,要维护最大值。因为要算最少的空位子,下面给出两种代码:
1、纯贪心&贪心:
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cctype>
#define maxn 50007
using namespace std;
int ans,n,m,k,w[maxn];
inline int qread() {
char c=getchar();int num=0,f=1;
for(;!isdigit(c);c=getchar()) if(c=='-') f=-1;
for(;isdigit(c);c=getchar()) num=num*10+c-'0';
return num*f;
}
struct node {
int u,v,c;
}e[maxn];
const int inf=0x7fffffff;
inline bool cmp(node a, node b) {
if(a.v!=b.v) return a.v<b.v;
return a.u<b.u;
}
int main() {
k=qread(),n=qread(),m=qread();
for(int i=1;i<=k;++i) e[i].u=qread(),e[i].v=qread(),e[i].c=qread();
sort(e+1,e+1+k,cmp);
for(int i=1;i<=k;++i) {
if(w[e[i].u]>=m) continue;
int minn=inf;
for(int j=e[i].u;j<=e[i].v;++j) {
minn=min(m-w[j],minn);
if(minn<=0) break;
}
if(minn>0) {
if(minn>=e[i].c) {
for(int j=e[i].u;j<e[i].v;++j)
w[j]+=e[i].c;
ans+=e[i].c;
}
else {
for(int j=e[i].u;j<e[i].v;++j)
w[j]+=minn;
ans+=minn;
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
return 0;
}2、线段树&贪心&排序:
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cctype>
#define maxn 20007
#define ls rt<<1
#define rs rt<<1|1
using namespace std;
const int inf=0x7fffffff;
int n,k,m,maxx[maxn<<2],lazy[maxn<<2],zrj,w[50007];
inline int qread() {
char c=getchar();int num=0,f=1;
for(;!isdigit(c);c=getchar()) if(c=='-') f=-1;
for(;isdigit(c);c=getchar()) num=num*10+c-'0';
return num*f;
}
struct node {
int u,v,c;
}e[50007];
inline bool cmp(node a, node b) {
if(a.v!=b.v) return a.v<b.v;
return a.u<b.u;
}
inline void pushup(int rt) {
maxx[rt]=max(maxx[ls],maxx[rs]);
}
inline void pushdown(int rt) {
if(lazy[rt]) {
maxx[ls]+=lazy[rt],lazy[ls]+=lazy[rt];
maxx[rs]+=lazy[rt],lazy[rs]+=lazy[rt];
lazy[rt]=0;
}
}
void modify(int rt, int l, int r, int L, int R, int val) {
if(L>r||R<l) return;
if(L<=l&&r<=R) {
lazy[rt]+=val,maxx[rt]+=val;
return;
}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
pushdown(rt);
modify(ls,l,mid,L,R,val),modify(rs,mid+1,r,L,R,val);
pushup(rt);
}
int cmax(int rt, int l, int r, int L, int R) {
if(L>r||R<l) return -inf;
if(L<=l&&r<=R) return maxx[rt];
int mid=(l+r)>>1,ans=-inf;
pushdown(rt);
if(L<=mid) ans=max(ans,cmax(ls,l,mid,L,R));
if(R>mid) ans=max(ans,cmax(rs,mid+1,r,L,R));
return ans;
}
int main() {
k=qread(),n=qread(),m=qread();
for(int i=1;i<=k;++i) e[i].u=qread(),e[i].v=qread(),e[i].c=qread();
sort(e+1,e+1+k,cmp);
for(int i=1;i<=k;++i) {
int p=cmax(1,1,n,e[i].u,e[i].v-1);
int minn=min(m-p,e[i].c);
zrj+=minn,w[i]+=minn;
modify(1,1,n,e[i].u,e[i].v-1,w[i]);
}
printf("%d\n",zrj);
return 0;
}2. 洛谷 P3128 [USACO15DEC]最大流Max Flow
题目描述
\(FJ\)给他的牛棚的\(N(2≤N≤50,000)\)个隔间之间安装了\(N-1\)根管道,隔间编号从\(1\)到\(N\)。所有隔间都被管道连通了。
\(FJ\)有\(K(1≤K≤100,000)\)条运输牛奶的路线,第\(i\)条路线从隔间\(s_i\)运输到隔间\(t_i\)。一条运输路线会给它的两个端点处的隔间以及中间途径的所有隔间带来一个单位的运输压力,你需要计算压力最大的隔间的压力是多少。
输入输出格式
输入格式:
The first line of the input contains \(N\) and \(K\).
The next \(N-1\) lines each contain two integers \(x\) and \(y\) \((x \ne y\)) describing a pipe
between stalls \(x\) and \(y\).
The next \(K\) lines each contain two integers \(s\) and \(t\) describing the endpoint
stalls of a path through which milk is being pumped.
输出格式:
An integer specifying the maximum amount of milk pumped through any stall in the
barn.
输入输出样例
输入样例#1:
5 10
3 4
1 5
4 2
5 4
5 4
5 4
3 5
4 3
4 3
1 3
3 5
5 4
1 5
3 4输出样例#1:
9思路:树链剖分+线段树,题目中给出的每组点就相当于是路径修改,也就是树链剖分里面的基本操作,要求输出的最大压力值的隔间就是一到n压力值的最大值,因此我们只需要再用线段树维护区间最大值就好了。
代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cctype>
#define maxn 50007
#define ls rt<<1
#define rs rt<<1|1
using namespace std;
int id[maxn],d[maxn],n,k,cnt,son[maxn],top[maxn],maxx[maxn<<2];
int head[maxn],num,fa[maxn],siz[maxn],lazy[maxn<<2];
inline int qread() {
char c=getchar();int num=0,f=1;
for(;!isdigit(c);c=getchar()) if(c=='-') f=-1;
for(;isdigit(c);c=getchar()) num=num*10+c-'0';
return num*f;
}
const int inf=0x7fffffff;
struct node {
int v,nxt;
}e[maxn<<1];
inline void ct(int u, int v) {
e[++num].v=v;
e[num].nxt=head[u];
head[u]=num;
}
void dfs1(int u) {
siz[u]=1;
for(int i=head[u];i;i=e[i].nxt) {
int v=e[i].v;
if(v!=fa[u]) {
d[v]=d[u]+1;
fa[v]=u;
dfs1(v);
siz[u]+=siz[v];
if(siz[v]>siz[son[u]]) son[u]=v;
}
}
}
void dfs2(int u, int t) {
id[u]=++cnt;
top[u]=t;
if(son[u]) dfs2(son[u],t);
for(int i=head[u];i;i=e[i].nxt) {
int v=e[i].v;
if(v!=fa[u]&&v!=son[u]) dfs2(v,v);
}
}
inline void pushup(int rt) {
maxx[rt]=max(maxx[ls],maxx[rs]);
}
inline void pushdown(int rt) {
if(lazy[rt]) {
lazy[ls]+=lazy[rt],maxx[ls]+=lazy[rt];
lazy[rs]+=lazy[rt],maxx[rs]+=lazy[rt];
lazy[rt]=0;
}
}
void modify(int rt, int l, int r, int L, int R, int val) {
if(L>r||R<l) return;
if(L<=l&&r<=R) {
lazy[rt]+=val,maxx[rt]+=val;
return;
}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
pushdown(rt);
modify(ls,l,mid,L,R,val),modify(rs,mid+1,r,L,R,val);
pushup(rt);
}
int cmax(int rt, int l, int r, int L, int R) {
if(L>r||R<l) return -inf;
if(L<=l&&r<=R) return maxx[rt];
int mid=(l+r)>>1,ans=-inf;
pushdown(rt);
if(L<=mid) ans=max(ans,cmax(ls,l,mid,L,R));
if(R>mid) ans=max(ans,cmax(rs,mid+1,r,L,R));
return ans;
}
void cal(int x, int y, int val) {
int fx=top[x],fy=top[y];
while(fx!=fy) {
if(d[fx]<d[fy]) swap(x,y),swap(fx,fy);
modify(1,1,cnt,id[fx],id[x],val);
x=fa[fx],fx=top[x];
}
if(id[x]>id[y]) swap(x,y);
modify(1,1,cnt,id[x],id[y],val);
}
int main() {
n=qread(),k=qread();
for(int i=1,u,v;i<n;++i) {
u=qread(),v=qread();
ct(u,v),ct(v,u);
}
dfs1(1);dfs2(1,1);
for(int i=1,u,v;i<=k;++i) {
u=qread(),v=qread();
cal(u,v,1);
}
printf("%d\n",cmax(1,1,cnt,1,cnt));
return 0;
}3. SP375 QTREE - Query on a tree
题意大意
给定\(n\)个点的树,边按输入顺序编号为\(1,2,...n-1\),要求作以下操作: CHANGE \(i\) \(t_i\) 将第\(i\)条边权值改为\(t_i\),QUERY \(a\) \(b\) 询问从\(a\)点到\(b\)点路径上的最大边权
有多组测试数据,每组数据以DONE结尾
题目描述
You are given a tree (an acyclic undirected connected graph) with N nodes, and edges numbered 1, 2, 3...N-1.
We will ask you to perfrom some instructions of the following form:
- CHANGE i ti : change the cost of the i-th edge to ti
or - QUERY a b : ask for the maximum edge cost on the path from node a to node b
输入输出格式
输入格式:
The first line of input contains an integer t, the number of test cases (t <= 20). t test cases follow.
For each test case:
- In the first line there is an integer N (N <= 10000),
- In the next N-1 lines, the i-th line describes the i-th edge: a line with three integers a b c denotes an edge between a, b of cost c (c <= 1000000),
- The next lines contain instructions "CHANGE i ti" or "QUERY a b",
- The end of each test case is signified by the string "DONE".
There is one blank line between successive tests.
输出格式:
For each "QUERY" operation, write one integer representing its result.
输入输出样例
输入样例#1:
1
3
1 2 1
2 3 2
QUERY 1 2
CHANGE 1 3
QUERY 1 2
DONE输出样例#1:
1
3思路:
其实这个题也不算特别的难,如果你做过有关换边权为点权的题目的话,比如……月下“毛景树”,旅游等。自我感觉难度都比这道题要大,并且都涉及到化边权为点权然后树链剖分。
不多说了,我们来看这个题,这道题与普通的树链剖分题目不同的是,这道题目给出的是边权,但是普通的树链剖分题目都是给出的点权,那,该怎么办呢?不难发现,每个点有且只有一条边连向它的父亲结点,诶??有且只有一条?那!!我们就可以用这个点的点权去代替它与它父亲之间边的边权呀!!那这不就又成了树链剖分板子题了嘛?!\(QwQ\)。还有一个坑就是最后查询的时候,因为LCA的点权不在查询的路径范围内,因此要排除掉。
洛谷上此题的c++评测有些问题,下面给出c的代码(memset必须要全写,不然没法AC,我也不知道为什么):
#include <ctype.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define maxn 10007
#define ls rt<<1
#define rs rt<<1|1
int id[maxn],d[maxn],n,cnt,son[maxn],top[maxn],maxx[maxn<<2],t;
int head[maxn],num,fa[maxn],siz[maxn],w[maxn],a[maxn];
char s[8];
struct node {
int v,w,nxt;
}e[maxn<<1];
int max(int a, int b) { return a > b ? a : b; }
#define swap(A, B) \
{ \
int __T = A; \
A = B; \
B = __T; \
}
void ct(int u, int v, int w) {
e[++num].v=v;
e[num].w=w;
e[num].nxt=head[u];
head[u]=num;
}
void pushup(int rt) {
maxx[rt]=max(maxx[ls],maxx[rs]);
}
void build(int rt, int l, int r) {
if(l==r) {
maxx[rt]=a[l];
return;
}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
build(ls,l,mid);
build(rs,mid+1,r);
pushup(rt);
}
void modify(int rt, int l, int r, int L, int val) {
if(l==r) {
maxx[rt]=val;
return;
}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(L<=mid) modify(ls,l,mid,L,val);
else modify(rs,mid+1,r,L,val);
pushup(rt);
}
int cmax(int rt, int l, int r, int L, int R) {
if(L<=l&&r<=R) return maxx[rt];
int ans=0;
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(L<=mid) ans=max(ans,cmax(ls,l,mid,L,R));
if(R>mid) ans=max(ans,cmax(rs,mid+1,r,L,R));
return ans;
}
void dfs1(int u) {
siz[u]=1;
for(int i=head[u];i;i=e[i].nxt) {
int v=e[i].v;
if(v!=fa[u]) {
d[v]=d[u]+1;
fa[v]=u;
w[v]=e[i].w;
dfs1(v);
siz[u]+=siz[v];
if(siz[v]>siz[son[u]]) son[u]=v;
}
}
}
void dfs2(int u, int t) {
id[u]=++cnt;
top[u]=t;
a[cnt]=w[u];
if(son[u]) dfs2(son[u],t);
for(int i=head[u];i;i=e[i].nxt) {
int v=e[i].v;
if(v!=fa[u]&&v!=son[u]) dfs2(v,v);
}
}
int query(int x, int y) {
int ans=0,fx=top[x],fy=top[y];
while(fx!=fy) {
if(d[fx]<d[fy]) {
swap(x,y);
swap(fx,fy);
}
ans=max(ans,cmax(1,1,n,id[fx],id[x]));
x=fa[fx],fx=top[x];
}
if(id[x]>id[y]) swap(x,y);
ans=max(ans,cmax(1,1,n,id[x]+1,id[y]));
return ans;
}
int main() {
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--) {
memset(head,0,sizeof(head));
memset(siz,0,sizeof(siz));
memset(id,0,sizeof(id));
memset(top,0,sizeof(top));
memset(son,0,sizeof(son));
memset(w,0,sizeof(w));
memset(maxx,0,sizeof(maxx));
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
memset(fa,0,sizeof(fa));
memset(d,0,sizeof(d));num=0;cnt=0;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1,u,v,w;i<n;++i) {
scanf("%d%d%d",&u,&v,&w);
ct(u,v,w),ct(v,u,w);
}
dfs1(1);dfs2(1,1);build(1,1,n);
while(1) {
scanf("%s",s);
if(s[0]=='D') break;
if(s[0]=='C') {
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
x=d[e[x*2-1].v]<d[e[x<<1].v]?e[x<<1].v:e[x*2-1].v;
modify(1,1,cnt,id[x],y);
}
if(s[0]=='Q') {
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
printf("%d\n",query(x,y));
}
}
}
return 0;
}接下来是在SPOJ上能够AC的c++代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#define maxn 10007
#define ls rt<<1
#define rs rt<<1|1
using namespace std;
int id[maxn],d[maxn],n,cnt,son[maxn],top[maxn],maxx[maxn<<2],t;
int head[maxn],num,fa[maxn],siz[maxn],w[maxn],a[maxn];
char s[8];
struct node {
int v,w,nxt;
}e[maxn<<1];
inline void ct(int u, int v, int w) {
e[++num].v=v;
e[num].w=w;
e[num].nxt=head[u];
head[u]=num;
}
inline void pushup(int rt) {
maxx[rt]=max(maxx[ls],maxx[rs]);
}
void build(int rt, int l, int r) {
if(l==r) {
maxx[rt]=a[l];
return;
}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
build(ls,l,mid);
build(rs,mid+1,r);
pushup(rt);
}
void modify(int rt, int l, int r, int L, int val) {
if(l==r) {
maxx[rt]=val;
return;
}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(L<=mid) modify(ls,l,mid,L,val);
else modify(rs,mid+1,r,L,val);
pushup(rt);
}
int cmax(int rt, int l, int r, int L, int R) {
if(L<=l&&r<=R) return maxx[rt];
int ans=0;
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(L<=mid) ans=max(ans,cmax(ls,l,mid,L,R));
if(R>mid) ans=max(ans,cmax(rs,mid+1,r,L,R));
return ans;
}
void dfs1(int u) {
siz[u]=1;
for(int i=head[u];i;i=e[i].nxt) {
int v=e[i].v;
if(v!=fa[u]) {
d[v]=d[u]+1;
fa[v]=u;
w[v]=e[i].w;
dfs1(v);
siz[u]+=siz[v];
if(siz[v]>siz[son[u]]) son[u]=v;
}
}
}
void dfs2(int u, int t) {
id[u]=++cnt;
top[u]=t;
a[cnt]=w[u];
if(son[u]) dfs2(son[u],t);
for(int i=head[u];i;i=e[i].nxt) {
int v=e[i].v;
if(v!=fa[u]&&v!=son[u]) dfs2(v,v);
}
}
int query(int x, int y) {
int ans=0,fx=top[x],fy=top[y];
while(fx!=fy) {
if(d[fx]<d[fy]) {
swap(x,y);
swap(fx,fy);
}
ans=max(ans,cmax(1,1,n,id[fx],id[x]));
x=fa[fx],fx=top[x];
}
if(id[x]>id[y]) swap(x,y);
ans=max(ans,cmax(1,1,n,id[x]+1,id[y]));
return ans;
}
int main() {
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--) {
memset(head,0,sizeof(head));
memset(siz,0,sizeof(siz));
memset(id,0,sizeof(id));
memset(top,0,sizeof(top));
memset(son,0,sizeof(son));
memset(w,0,sizeof(w));
memset(maxx,0,sizeof(maxx));
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
memset(fa,0,sizeof(fa));
memset(d,0,sizeof(d));num=0;cnt=0;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1,u,v,w;i<n;++i) {
scanf("%d%d%d",&u,&v,&w);
ct(u,v,w),ct(v,u,w);
}
dfs1(1);dfs2(1,1);build(1,1,n);
while(1) {
scanf("%s",s);
if(s[0]=='D') break;
if(s[0]=='C') {
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
x=d[e[x*2-1].v]<d[e[x<<1].v]?e[x<<1].v:e[x*2-1].v;
modify(1,1,cnt,id[x],y);
}
if(s[0]=='Q') {
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
printf("%d\n",query(x,y));
}
}
}
return 0;
}4. CF438D The Child and Sequence
题意大意
给定数列,区间查询和,区间取模,单点修改。
\(n\),\(m\)小于\(10^5\)
题目描述
At the children's day, the child came to Picks's house, and messed his house up. Picks was angry at him. A lot of important things were lost, in particular the favorite sequence of Picks.
Fortunately, Picks remembers how to repair the sequence. Initially he should create an integer array \(a[1],a[2],...,a[n]\). Then he should perform a sequence of mm operations. An operation can be one of the following:
- Print operation \(l,r\) . Picks should write down the value of
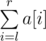 .
. - Modulo operation \(l,r,x\) . Picks should perform assignment \(a[i]=a[i] mod x\) for each \(i\) \((l<=i<=r)\).
- Set operation \(k,x\) . Picks should set the value of \(a[k]\) to \(x\) (in other words perform an assignment \(a[k]=x\)).
Can you help Picks to perform the whole sequence of operations?
输入输出格式
输入格式:
The first line of input contains two integer: \(n,m\) \((1<=n,m<=10^{5})\) . The second line contains nnintegers, separated by space: \(a[1],a[2],...,a[n] (1<=a[i]<=10^{9})\) — initial value of array elements.
Each of the next mm lines begins with a number typetype 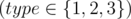 .
.
- If \(type=1\) , there will be two integers more in the line: \(l,r (1<=l<=r<=n)\) , which correspond the operation \(1\).
- If \(type=2\) , there will be three integers more in the line: \(l,r,x (1<=l<=r<=n; 1<=x<=10^{9})\) , which correspond the operation \(2\).
- If \(type=3\), there will be two integers more in the line: \(k,x (1<=k<=n; 1<=x<=10^{9})\) , which correspond the operation \(3\).
输出格式:
For each operation \(1\), please print a line containing the answer. Notice that the answer may exceed the \(32\)-bit integer.
输入输出样例
输入样例#1:
5 5
1 2 3 4 5
2 3 5 4
3 3 5
1 2 5
2 1 3 3
1 1 3输出样例#1:
8
5输入样例#2:
10 10
6 9 6 7 6 1 10 10 9 5
1 3 9
2 7 10 9
2 5 10 8
1 4 7
3 3 7
2 7 9 9
1 2 4
1 6 6
1 5 9
3 1 10输出样例#2:
49
15
23
1
9说明
Consider the first testcase:
- At first, a={1,2,3,4,5}.
- After operation 1 , a={1,2,3,0,1}.
- After operation 2 , a={1,2,5,0,1}.
- At operation 3 , 2+5+0+1=8.
- After operation 4 , a={1,2,2,0,1}.
- At operation 5 , 1+2+2=5.
思路:
题目大意:给定数列,区间查询和,区间取模,单点修改。
\(n,m\)小于\(10^5\)
查询区间和和单点修改就不用说了吧,线段树基本操作,那??对于这道题目的区间修改该怎么处理呢??不难发现,一个数模两次同样的数时没有任何意义的,而且一个数模一个比它大的数也是没有意义的?!!!那么,我们便可以采用一种暴力的思想,去修改每一个位置,每次判断一下区间最大值是不是比模数大即可。因为是暴力修改,所以也无需\(pushdown\),那么代码应该就很好写了吧,也不算太长。
下面是我的代码,仅供参考,毕竟太丑了:
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cctype>
#define maxn 100007
#define ls rt<<1
#define rs rt<<1|1
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
int n,m,maxx[maxn<<2];
ll sum[maxn<<2];
inline int qread() {
char c=getchar();int num=0,f=1;
for(;!isdigit(c);c=getchar()) if(c=='-') f=-1;
for(;isdigit(c);c=getchar()) num=num*10+c-'0';
return num*f;
}
inline void pushup(int rt) {
sum[rt]=sum[ls]+sum[rs];
maxx[rt]=max(maxx[ls],maxx[rs]);
}
void build(int rt, int l, int r) {
if(l==r) {
maxx[rt]=sum[rt]=qread();
return;
}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
build(ls,l,mid);
build(rs,mid+1,r);
pushup(rt);
}
void add(int rt, int l, int r, int L, int val) {
if(l==r) {
maxx[rt]=sum[rt]=val;
return;
}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(L<=mid) add(ls,l,mid,L,val);
else add(rs,mid+1,r,L,val);
pushup(rt);
}
ll csum(int rt, int l, int r, int L, int R) {
if(L<=l&&r<=R) return sum[rt];
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
ll ans=0;
if(L<=mid) ans+=csum(ls,l,mid,L,R);
if(R>mid) ans+=csum(rs,mid+1,r,L,R);
return ans;
}
void modify(int rt, int l, int r, int L, int R, int p) {
if(maxx[rt]<p) return;
if(l==r) {
sum[rt]%=p;maxx[rt]%=p;
return;
}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(L<=mid) modify(ls,l,mid,L,R,p);
if(R>mid) modify(rs,mid+1,r,L,R,p);
pushup(rt);
}
int main() {
n=qread(),m=qread();
build(1,1,n);
for(int i=1,k,x,y,z;i<=m;++i) {
k=qread(),x=qread(),y=qread();
if(k==1) printf("%lld\n",csum(1,1,n,x,y));
if(k==2) {
z=qread();
modify(1,1,n,x,y,z);
}
if(k==3) add(1,1,n,x,y);
}
return 0;
}5. 洛谷P3398 仓鼠找sugar
题目描述
小仓鼠的和他的基\((mei)\)友\((zi)sugar\)住在地下洞穴中,每个节点的编号为\(1\)~\(n\)。地下洞穴是一个树形结构。这一天小仓鼠打算从从他的卧室\((a)\)到餐厅\((b)\),而他的基友同时要从他的卧室\((c)\)到图书馆\((d)\)。他们都会走最短路径。现在小仓鼠希望知道,有没有可能在某个地方,可以碰到他的基友?
小仓鼠那么弱,还要天天被\(zzq\)大爷虐,请你快来救救他吧!
输入输出格式
输入格式:
第一行两个正整数\(n\)和\(q\),表示这棵树节点的个数和询问的个数。
接下来\(n-1\)行,每行两个正整数\(u\)和\(v\),表示节点\(u\)到节点\(v\)之间有一条边。
接下来\(q\)行,每行四个正整数\(a\)、\(b\)、\(c\)和\(d\),表示节点编号,也就是一次询问,其意义如上。
输出格式:
对于每个询问,如果有公共点,输出大写字母“Y”;否则输出“N”。
输入输出样例
输入样例#1:
5 5
2 5
4 2
1 3
1 4
5 1 5 1
2 2 1 4
4 1 3 4
3 1 1 5
3 5 1 4输出样例#1:
Y
N
Y
Y
Y说明
本题时限1s,内存限制128M,因新评测机速度较为接近NOIP评测机速度,请注意常数问题带来的影响。
\(20\%\)的数据 \(n<=200,q<=200\)
\(40\%\)的数据 \(n<=2000,q<=2000\)
\(70\%\)的数据 \(n<=50000,q<=50000\)
\(100\%\)的数据 \(n<=100000,q<=100000\)
思路:
其实,多画几个图模拟一下,可以发现如下一个神奇的规律:
如果两条路径相交,那么一定有一条路径的LCA在另一条路径上
而判断一个节点\(x\),是否在路径\(a\)-\(b\)上需要满足如下几个条件
- d[x]>=d[LCA(a,b)]
- LCA(a,x)=x或LCA(b,x)=x;其中d数组代表深度。
所以分两种情况讨论一下即可
时间复杂度\(O(n log n)\),下面是树剖求\(LCA\)的代码,倍增照样可以做,就是慢了点。
代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cctype>
#define maxn 100007
using namespace std;
int num,head[maxn],n,d[maxn],son[maxn],top[maxn],siz[maxn];
int cnt,id[maxn],fa[maxn],m;
inline int qread() {
char c=getchar();int num=0,f=1;
for(;!isdigit(c);c=getchar()) if(c=='-') f=-1;
for(;isdigit(c);c=getchar()) num=num*10+c-'0';
return num*f;
}
struct node {
int v,nxt;
}e[maxn<<1];
inline void ct(int u, int v) {
e[++num].v=v;
e[num].nxt=head[u];
head[u]=num;
}
void dfs1(int u) {
siz[u]=1;
for(int i=head[u];i;i=e[i].nxt) {
int v=e[i].v;
if(v!=fa[u]) {
d[v]=d[u]+1;
fa[v]=u;
dfs1(v);
siz[u]+=siz[v];
if(siz[v]>siz[son[u]]) son[u]=v;
}
}
}
void dfs2(int u, int t) {
id[u]=++cnt;
top[u]=t;
if(son[u]) dfs2(son[u],t);
for(int i=head[u];i;i=e[i].nxt) {
int v=e[i].v;
if(v!=fa[u]&&v!=son[u]) dfs2(v,v);
}
}
inline int lca(int x, int y) {
int fx=top[x],fy=top[y];
while(fx!=fy) {
if(d[fx]<d[fy]) swap(x,y),swap(fx,fy);
x=fa[fx],fx=top[x];
}
return d[x]>d[y]?y:x;
}
int main() {
n=qread(),m=qread();
for(int i=1,u,v;i<n;++i) {
u=qread(),v=qread();
ct(u,v),ct(v,u);
}
dfs1(1);dfs2(1,1);
for(int i=1,a,b,c,p;i<=m;++i) {
a=qread(),b=qread(),c=qread(),p=qread();
int zrj=lca(a,b),cyh=lca(c,p);
if(d[zrj]<d[cyh]) swap(zrj,cyh),swap(a,c),swap(b,p);
if(lca(zrj,c)==zrj||lca(zrj,p)==zrj) printf("Y\n");
else printf("N\n");
}
return 0;
}6. 洛谷P2146 [NOI2015]软件包管理器
题目描述
\(Linux\)用户和\(OSX\)用户一定对软件包管理器不会陌生。通过软件包管理器,你可以通过一行命令安装某一个软件包,然后软件包管理器会帮助你从软件源下载软件包,同时自动解决所有的依赖(即下载安装这个软件包的安装所依赖的其它软件包),完成所有的配置。\(Debian/Ubuntu\)使用的\(apt-get\),\(Fedora/CentOS\)使用的\(yum\),以及\(OSX\)下可用的\(homebrew\)都是优秀的软件包管理器。
你决定设计你自己的软件包管理器。不可避免地,你要解决软件包之间的依赖问题。如果软件包\(A\)依赖软件包\(B\),那么安装软件包\(A\)以前,必须先安装软件包\(B\)。同时,如果想要卸载软件包\(B\),则必须卸载软件包\(A\)。现在你已经获得了所有的软件包之间的依赖关系。而且,由于你之前的工作,除0号软件包以外,在你的管理器当中的软件包都会依赖一个且仅一个软件包,而0号软件包不依赖任何一个软件包。依赖关系不存在环(若有\(m(m≥2)\)个软件包\(A1,A2,A3,⋯,Am\),其中\(A1\)依赖\(A2\),\(A2\)依赖\(A3\),\(A3\)依赖\(A4\),……,\(A[m-1]\)依赖\(Am\),而\(Am\)依赖\(A1\),则称这\(m\)个软件包的依赖关系构成环),当然也不会有一个软件包依赖自己。
现在你要为你的软件包管理器写一个依赖解决程序。根据反馈,用户希望在安装和卸载某个软件包时,快速地知道这个操作实际上会改变多少个软件包的安装状态(即安装操作会安装多少个未安装的软件包,或卸载操作会卸载多少个已安装的软件包),你的任务就是实现这个部分。注意,安装一个已安装的软件包,或卸载一个未安装的软件包,都不会改变任何软件包的安装状态,即在此情况下,改变安装状态的软件包数为\(0\)。
输入输出格式
输入格式:
从文件\(manager.in\)中读入数据。
输入文件的第\(1\)行包含\(1\)个整数\(n\),表示软件包的总数。软件包从\(0\)开始编号。
随后一行包含\(n−1\)个整数,相邻整数之间用单个空格隔开,分别表示\(1,2,3,⋯,n−2,n−1\)号软件包依赖的软件包的编号。
接下来一行包含\(1\)个整数\(q\),表示询问的总数。之后\(q\)行,每行\(1\)个询问。询问分为两种:
\(install\) \(x\):表示安装软件包\(x\)
\(uninstall\) \(x\):表示卸载软件包\(x\)
你需要维护每个软件包的安装状态,一开始所有的软件包都处于未安装状态。
对于每个操作,你需要输出这步操作会改变多少个软件包的安装状态,随后应用这个操作(即改变你维护的安装状态)。
输出格式:
输出到文件\(manager.out\)中。
输出文件包括\(q\)行。
输出文件的第\(i\)行输出\(1\)个整数,为第i步操作中改变安装状态的软件包数。
输入输出样例
输入样例#1:
7
0 0 0 1 1 5
5
install 5
install 6
uninstall 1
install 4
uninstall 0输出样例#1:
3
1
3
2
3输入样例#2:
10
0 1 2 1 3 0 0 3 2
10
install 0
install 3
uninstall 2
install 7
install 5
install 9
uninstall 9
install 4
install 1
install 9输出样例#2:
1
3
2
1
3
1
1
1
0
1说明
【样例说明 1】
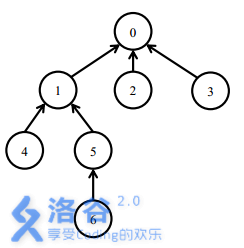
一开始所有的软件包都处于未安装状态。
安装\(5\)号软件包,需要安装\(0\),\(1\),\(5\)三个软件包。
之后安装\(6\)号软件包,只需要安装\(6\)号软件包。此时安装了\(0\),\(1\),\(5\),\(6\)四个软件包。
卸载\(1\)号软件包需要卸载\(1\),\(5\),\(6\)三个软件包。此时只有\(0\)号软件包还处于安装状态。
之后安装\(4\)号软件包,需要安装\(1\),\(4\)两个软件包。此时\(0\),\(1\),\(4\)处在安装状态。最后,卸载\(0\)号软件包会卸载所有的软件包。`
【数据范围】
【时限1s,内存512M】
思路:根据题意可以知道,题目中每个点只有两个状态,安装和未安装,我们可以用\(0\)来表示安装,\(1\)来表示未安装,那么对于\(install\)类型的询问,就是从被询问的点到根节点最短路径的\(1\)的个数。对于\(uninstall\)类型的询问,就是被询问的点的子树点的个数减去这个点子树中点权为\(1\)的点的个数,那代码就很好写了。直接用树剖+线段树来维护即可。
代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cctype>
#define maxn 100007
#define ls rt<<1
#define rs rt<<1|1
using namespace std;
int n,m,id[maxn],cnt,num,son[maxn],fa[maxn],siz[maxn];
int d[maxn],lazy[maxn<<2],sum[maxn<<2],top[maxn],head[maxn];
char s[8];
inline int qread() {
char c=getchar();int num=0,f=1;
for(;!isdigit(c);c=getchar()) if(c=='-') f=-1;
for(;isdigit(c);c=getchar()) num=num*10+c-'0';
return num*f;
}
struct node {
int v,nxt;
}e[maxn<<1];
inline void ct(int u, int v) {
e[++num].v=v;
e[num].nxt=head[u];
head[u]=num;
}
void dfs1(int u) {
siz[u]=1;
for(int i=head[u];i;i=e[i].nxt) {
int v=e[i].v;
if(v!=fa[u]) {
d[v]=d[u]+1;
fa[v]=u;
dfs1(v);
siz[u]+=siz[v];
if(siz[v]>siz[son[u]]) son[u]=v;
}
}
}
void dfs2(int u, int t) {
id[u]=++cnt;
top[u]=t;
if(son[u]) dfs2(son[u],t);
for(int i=head[u];i;i=e[i].nxt) {
int v=e[i].v;
if(v!=fa[u]&&v!=son[u]) dfs2(v,v);
}
}
inline void pushup(int rt) {
sum[rt]=sum[ls]+sum[rs];
}
inline void pushdown(int rt, int len) {
if(lazy[rt]>=0) {
lazy[ls]=lazy[rs]=lazy[rt];
sum[ls]=(len-(len>>1))*lazy[rt];
sum[rs]=(len>>1)*lazy[rt];
lazy[rt]=-1;
}
}
void build(int rt, int l, int r) {
lazy[rt]=-1;
if(l==r) {
sum[rt]=1;
return;
}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
build(ls,l,mid);
build(rs,mid+1,r);
pushup(rt);
}
void modify(int rt, int l, int r, int L, int R, int val) {
if(L>r||R<l) return;
if(L<=l&&r<=R) {
sum[rt]=val*(r-l+1);
lazy[rt]=val;
return;
}
pushdown(rt,r-l+1);
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(L<=mid) modify(ls,l,mid,L,R,val);
if(R>mid) modify(rs,mid+1,r,L,R,val);
pushup(rt);
}
int csum(int rt, int l, int r, int L, int R) {
if(L>r||R<l) return 0;
if(L<=l&&r<=R) return sum[rt];
int mid=(l+r)>>1,ans=0;
pushdown(rt,r-l+1);
if(L<=mid) ans+=csum(ls,l,mid,L,R);
if(R>mid) ans+=csum(rs,mid+1,r,L,R);
return ans;
}
int query(int x, int y) {
int fx=top[x],fy=top[y],ans=0;
while(fx!=fy) {
if(d[fx]<d[fy]) swap(x,y),swap(fx,fy);
ans+=csum(1,1,cnt,id[fx],id[x]);
x=fa[fx],fx=top[x];
}
if(id[x]>id[y]) swap(x,y);
ans+=csum(1,1,cnt,id[x],id[y]);
return ans;
}
void cal(int x, int y, int val) {
int fx=top[x],fy=top[y];
while(fx!=fy) {
if(d[fx]<d[fy]) swap(x,y),swap(fx,fy);
modify(1,1,cnt,id[fx],id[x],val);
x=fa[fx],fx=top[x];
}
if(id[x]>id[y]) swap(x,y);
modify(1,1,cnt,id[x],id[y],val);
}
int main() {
n=qread();
for(int i=2,v;i<=n;++i) {
v=qread()+1;
ct(v,i);ct(i,v);
}
dfs1(1);dfs2(1,1);
build(1,1,n);
m=qread();
for(int i=1,x;i<=m;++i) {
scanf("%s",s);x=qread()+1;
if(s[0]=='i') {
printf("%d\n",query(1,x));
cal(1,x,0);
}
else {
printf("%d\n",siz[x]-csum(1,1,n,id[x],id[x]+siz[x]-1));
modify(1,1,n,id[x],id[x]+siz[x]-1,1);
}
}
return 0;
}



 京公网安备 11010502036488号
京公网安备 11010502036488号