前言
随着Android应用开发技术的不断发展和成熟,很开发者越来越关注着Android应用架构的设计。目前,Android的应用架构主要有MVC、MVP和MVVM模式,我们就来说一下MVVM模式。
MVP模式
MVVM模式可以说是MVP模式的进一步发展,所以先来了解一下MVP模式。
MVP (Model-View-Presenter) 模式的结构如下图所示:

MVP模式将应用分为三层:Model层主要负责数据的提供,View层主要负责界面的显示,Presenter层主要负责业务逻辑的处理。
在MVP模式中,Model层和View层不能直接通信,Presenter层负责充当中间人,实现Model层和View层之间的间接通信。View层和Presenter层互相持有对方的引用,实现View层和Presenter层之间的通信。
MVP模式的主要优点是:分离了Model层和View层,分离了视图操作和业务逻辑,降低了耦合。
MVVM模式
MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel) 模式的结构如下图所示:

MVVM模式与MVP模式一样,也将应用分为三层,并且各个对应的层的职责相似:
- Model层,主要负责数据的提供。Model层提供业务逻辑的数据结构(比如,实体类),提供数据的获取(比如,从本地数据库或者远程网络获取数据),提供数据的存储。
- View层,主要负责界面的显示。View层不涉及任何的业务逻辑处理,它持有ViewModel层的引用,当需要进行业务逻辑处理时通知ViewModel层。
- ViewModel层,主要负责业务逻辑的处理。ViewModel层不涉及任何的视图操作。通过官方提供的Data Binding库,View层和ViewModel层中的数据可以实现绑定,ViewModel层中数据的变化可以自动通知View层进行更新,因此ViewModel层不需要持有View层的引用。ViewModel层可以看作是View层的数据模型和Presenter层的结合。
MVVM模式与MVP模式最大的区别在于:ViewModel层不持有View层的引用。这样进一步降低了耦合,View层代码的改变不会影响到ViewModel层。
MVVM模式相对于MVP模式主要有如下优点:
- 进一步降低了耦合。ViewModel层不持有View层的引用,当View层发生改变时,只要View层绑定的数据不变,那么ViewModel层就不需要改变。而在MVP模式下,当View层发生改变时,操作视图的接口就要进行相应的改变,那么Presenter层就需要修改了。
- 不用再编写很多样板代码。通过官方的Data Binding库,UI和数据之间可以实现绑定,不用再编写大量的findViewById()和操作视图的代码了。总之,Activity/Fragment的代码可以做到相当简洁。
例子
下面举一个简单的例子来实践MVVM模式。完整的项目代码可以去GitHub上查看:
例子实现的主要功能是:点击按钮网络查询天气,查询成功后在界面上显示天气信息。主界面如下图所示:

MVVM模式的代码组织结构建议按照 业务功能 进行划分,具体操作是:每个业务功能独立一个包存放,每个业务功能包下面再按Model、View、ViewModel分包存放。所有的Model存放在model包下面,所有的Activity和Fragment存放在activity包下面,所有的ViewModel存放在viewmodel包下面。该例子比较简单,只有一个weather业务功能模块,最终的代码组织结构如下图所示:
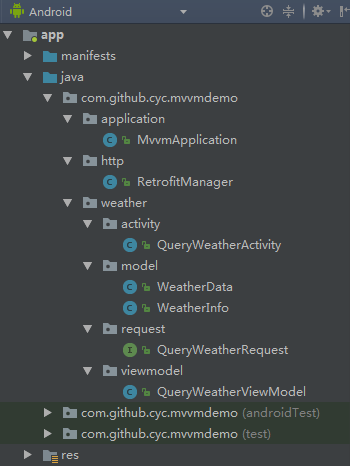 编写Model
编写Model
查询杭州天气的URL为:
访问该URL将返回一串JSON字符串,如下所示:
{"weatherinfo":{"city":"杭州","cityid":"101210101","temp1":"5℃","temp2":"20℃","weather":"晴转多云","img1":"n0.gif","img2":"d1.gif","ptime":"18:00"}}
按照此JSON字符串,可以编写相应的实体类。WeatherData类的代码如下所示:
public class WeatherData {
private WeatherInfo weatherinfo;
public WeatherInfo getWeatherinfo() {
return weatherinfo;
}
public void setWeatherinfo(WeatherInfo weatherinfo) {
this.weatherinfo = weatherinfo;
}
}
WeatherInfo类的代码如下所示:
public class WeatherInfo {
private String city;
private String cityid;
private String temp1;
private String temp2;
private String weather;
private String img1;
private String img2;
private String ptime;
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public String getCityid() {
return cityid;
}
public void setCityid(String cityid) {
this.cityid = cityid;
}
public String getTemp1() {
return temp1;
}
public void setTemp1(String temp1) {
this.temp1 = temp1;
}
public String getTemp2() {
return temp2;
}
public void setTemp2(String temp2) {
this.temp2 = temp2;
}
public String getWeather() {
return weather;
}
public void setWeather(String weather) {
this.weather = weather;
}
public String getImg1() {
return img1;
}
public void setImg1(String img1) {
this.img1 = img1;
}
public String getImg2() {
return img2;
}
public void setImg2(String img2) {
this.img2 = img2;
}
public String getPtime() {
return ptime;
}
public void setPtime(String ptime) {
this.ptime = ptime;
}
}
编写ViewModel
ViewModel不涉及任何的视图操作,只进行业务逻辑的处理。通过官方提供的Data Binding库,当ViewModel中的数据发生变化时,UI将自动更新。QueryWeatherViewModel的代码如下所示:
public class QueryWeatherViewModel {
private static final String TAG = "QueryWeatherViewModel";
public final ObservableBoolean loading = new ObservableBoolean(false);
public final ObservableBoolean loadingSuccess = new ObservableBoolean(false);
public final ObservableBoolean loadingFailure = new ObservableBoolean(false);
public final ObservableField<String> city = new ObservableField<>();
public final ObservableField<String> cityId = new ObservableField<>();
public final ObservableField<String> temp1 = new ObservableField<>();
public final ObservableField<String> temp2 = new ObservableField<>();
public final ObservableField<String> weather = new ObservableField<>();
public final ObservableField<String> time = new ObservableField<>();
private Call<WeatherData> mCall;
public QueryWeatherViewModel() {
}
public void queryWeather() {
loading.set(true);
loadingSuccess.set(false);
loadingFailure.set(false);
mCall = RetrofitManager.get()
.create(QueryWeatherRequest.class)
.queryWeather();
mCall.enqueue(new Callback<WeatherData>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(Call<WeatherData> call, Response<WeatherData> response) {
WeatherInfo weatherInfo = response.body().getWeatherinfo();
city.set(weatherInfo.getCity());
cityId.set(weatherInfo.getCityid());
temp1.set(weatherInfo.getTemp1());
temp2.set(weatherInfo.getTemp2());
weather.set(weatherInfo.getWeather());
time.set(weatherInfo.getPtime());
loading.set(false);
loadingSuccess.set(true);
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Call<WeatherData> call, Throwable t) {
if (call.isCanceled()) {
Log.i(TAG, "call is canceled.");
} else {
loading.set(false);
loadingFailure.set(true);
}
}
});
}
public void cancelRequest() {
if (mCall != null) {
mCall.cancel();
}
}
}
编写View
View不涉及任何的业务逻辑处理,只进行界面的显示。在xml布局文件中,通过官方提供的Data Binding库,将UI与ViewModel中的数据进行绑定,当ViewModel中的数据发生变化时,UI将自动更新。xml布局文件的代码如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<data>
<import type="android.view.View" />
<variable
name="viewModel"
type="com.github.cyc.mvvmdemo.weather.viewmodel.QueryWeatherViewModel" />
</data>
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="@dimen/default_content_padding"
tools:context="com.github.cyc.mvvmdemo.weather.activity.QueryWeatherActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_query_weather"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:text="@string/query_weather"
android:enabled="@{viewModel.loading ? false : true}"
android:onClick="@{() -> viewModel.queryWeather()}" />
<RelativeLayout
android:id="@+id/vg_weather_info"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/btn_query_weather"
android:layout_marginTop="@dimen/query_weather_margin"
android:visibility="@{viewModel.loadingSuccess ? View.VISIBLE : View.GONE}">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_city"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textStyle="bold"
android:text="@string/city" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_city_value"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/tv_city"
android:layout_alignBottom="@id/tv_city"
android:text="@{viewModel.city}"
tools:text="杭州" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_city_id"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/tv_city"
android:layout_marginTop="@dimen/query_weather_margin"
android:textStyle="bold"
android:text="@string/city_id" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_city_id_value"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/tv_city_id"
android:layout_alignBottom="@id/tv_city_id"
android:text="@{viewModel.cityId}"
tools:text="101210101" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_temp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/tv_city_id"
android:layout_marginTop="@dimen/query_weather_margin"
android:textStyle="bold"
android:text="@string/temperature" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_temp1_value"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/tv_temp"
android:layout_alignBottom="@id/tv_temp"
android:text="@{viewModel.temp1}"
tools:text="5℃" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_tilde"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/tv_temp1_value"
android:layout_alignBottom="@id/tv_temp"
android:text="@string/tilde" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_temp2_value"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/tv_tilde"
android:layout_alignBottom="@id/tv_temp"
android:text="@{viewModel.temp2}"
tools:text="10℃" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_weather"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/tv_temp"
android:layout_marginTop="@dimen/query_weather_margin"
android:textStyle="bold"
android:text="@string/weather" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_weather_value"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/tv_weather"
android:layout_alignBottom="@id/tv_weather"
android:text="@{viewModel.weather}"
tools:text="晴" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_time"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/tv_weather"
android:layout_marginTop="@dimen/query_weather_margin"
android:textStyle="bold"
android:text="@string/release_time" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_time_value"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/tv_time"
android:layout_alignBottom="@id/tv_time"
android:text="@{viewModel.time}"
tools:text="10:00" />
</RelativeLayout>
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/pb_progress"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:visibility="@{viewModel.loading ? View.VISIBLE : View.GONE}" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_query_failure"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:text="@string/query_failure"
android:visibility="@{viewModel.loadingFailure ? View.VISIBLE : View.GONE}" />
</RelativeLayout>
</layout>
在Activity中,通过官方提供的Data Binding库加载布局文件,创建ViewModel,并绑定View和ViewModel。QueryWeatherActivity的代码如下所示:
public class QueryWeatherActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
// ViewModel
private QueryWeatherViewModel mViewModel;
// DataBinding
private ActivityQueryWeatherBinding mDataBinding;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
mDataBinding = DataBindingUtil.setContentView(this, R.layout.activity_query_weather);
// 创建ViewModel
mViewModel = new QueryWeatherViewModel();
// 绑定View和ViewModel
mDataBinding.setViewModel(mViewModel);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
// 取消请求
mViewModel.cancelRequest();
}
}
总结
MVVM模式有三层:Model层主要负责数据的提供,View层主要负责界面的显示,ViewModel层主要负责业务逻辑的处理。各个层职责单一不同,但他们都结构清晰,应用起来十分的便捷
Android零基础系列教程:Android基础课程UI-动画_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
本文转自 Android | Android应用架构之MVVM模式_cyc的专栏-CSDN博客_android mvvm如有侵权,请联系删除。




 京公网安备 11010502036488号
京公网安备 11010502036488号